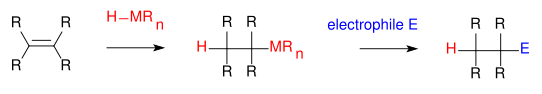Hydrometalation (hydrometallation) is a type of chemical reaction in organometallic chemistry in which a chemical compound with a hydrogen to metal bond (M-H, metal hydride) adds to compounds with an unsaturated bond like an alkene (RC=CR) forming a new compound with a carbon to metal bond (RHC-CRM).[1] The metal is less electronegative than hydrogen, the reverse reaction is beta-hydride elimination. The reaction is structurally related to carbometalation. When the substrate is an alkyne the reaction product is a vinylorganometallic.
Examples are hydroboration, hydroalumination, hydrosilylation and hydrozirconation.
References
edit- ^ Elschenbroich, C. ”Organometallics” (2006) Wiley-VCH: Weinheim. ISBN 3-527-29390-6