The Qing dynasty (/tʃɪŋ/ CHING), officially the Great Qing,[b] was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and an early modern empire in East Asia. The last imperial dynasty in Chinese history, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the Ming dynasty and succeeded by the Republic of China. At its height of power, the empire stretched from the Sea of Japan in the east to the Pamir Mountains in the west, and from the Mongolian Plateau in the north to the South China Sea in the south. Originally emerging from the Later Jin dynasty founded in 1616 and proclaimed in Shenyang in 1636, the dynasty seized control of the Ming capital Beijing and North China in 1644, traditionally considered the start of the dynasty's rule.[a] The dynasty lasted until the Xinhai Revolution of October 1911 led to the abdication of the last emperor in February 1912. The multi-ethnic Qing dynasty assembled the territorial base for modern China. The Qing controlled the most territory of any dynasty in Chinese history, and in 1790 represented the fourth-largest empire in world history to that point. With over 426 million citizens in 1907,[15] it was the most populous country in the world at the time.
Great Qing | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1636/1644[a]–1912 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Flag (1889–1912)
| |||||||||||||||||||||
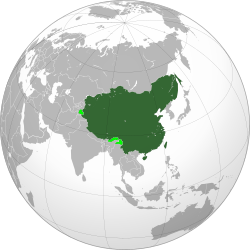 The Qing dynasty at its greatest extent in 1760, with modern borders shown for the rest of the world. Territory claimed but not controlled is shown in light green. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Capital and largest city | Beijing | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Official languages | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Ethnic groups | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Religion | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Demonym(s) | Chinese | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Government | Absolute monarchy | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Emperor | |||||||||||||||||||||
• 1636–1643 (proclaimed in Shenyang) | Chongde Emperor | ||||||||||||||||||||
• 1644–1661 (first in Beijing) | Shunzhi Emperor | ||||||||||||||||||||
• 1908–1912 (last) | Xuantong Emperor | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Regent | |||||||||||||||||||||
• 1643–1650 | Dorgon, Prince Rui | ||||||||||||||||||||
• 1908–1911 | Zaifeng, Prince Chun | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Prime Minister | |||||||||||||||||||||
• 1911 | Yikuang, Prince Qing | ||||||||||||||||||||
• 1911–1912 | Yuan Shikai | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Legislature |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Historical era | Late modern | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 1636 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 1644–1662 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 1687–1758 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 1747–1792 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 1839–1842 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 1850–1864 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 1856–1860 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 1861–1895 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 1894–1895 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 1898 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 1900–1901 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 1901–1911 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 1911–1912 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 12 February 1912 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 1700[13] | 8,800,000 km2 (3,400,000 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 1790[13] | 14,700,000 km2 (5,700,000 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 1860[13] | 13,400,000 km2 (5,200,000 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 1908[14] | 11,350,000 km2 (4,380,000 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Population | |||||||||||||||||||||
• 1907 estimate | 426,000,000[15] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Currency | |||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| Qing dynasty | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chinese name | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chinese | 清朝 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dynastic name | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chinese | 大清 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Literal meaning | Great Qing | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mongolian name | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mongolian Cyrillic | Дайчин Улс | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mongolian script |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Manchu name | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Manchu script |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Abkai | Daiqing gurun | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Möllendorff | Daicing gurun | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Nurhaci, leader of the Jianzhou Jurchens and House of Aisin-Gioro who was also a vassal of the Ming dynasty,[16][17] unified Jurchen clans (known later as Manchus) and founded the Later Jin dynasty in 1616, renouncing the Ming overlordship. As the founding Khan of the Manchu state he established the Eight Banners military system, and his son Hong Taiji was declared Emperor of the Great Qing in 1636. As Ming control disintegrated, peasant rebels captured Beijing as the short-lived Shun dynasty, but the Ming general Wu Sangui opened the Shanhai Pass to the Qing army, which defeated the rebels, seized the capital, and took over the government in 1644 under the Shunzhi Emperor and his prince regent. While the Qing became a Chinese empire, resistance from Ming rump regimes and the Revolt of the Three Feudatories delayed the complete conquest until 1683, which marked the beginning of the High Qing era. As an emperor of Manchu ethnic origin, the Kangxi Emperor (1661–1722) consolidated control, relished the role of a Confucian ruler, patronised Buddhism (including Tibetan Buddhism), encouraged scholarship, population and economic growth. Han officials worked under or in parallel with Manchu officials.
To maintain prominence over its neighbors, the Qing leveraged and adapted the traditional tributary system employed by previous dynasties, enabling their continued predominance in affairs with countries on its periphery like Joseon Korea and the Lê dynasty in Vietnam, while extending its control over Inner Asia including Tibet, Mongolia, and Xinjiang. The Qing dynasty reached its apex during the reign of the Qianlong Emperor (1735–1796), who led the Ten Great Campaigns of conquest, and personally supervised Confucian cultural projects. After his death, the dynasty faced internal revolts, economic disruption, official corruption, foreign intrusion, and the reluctance of Confucian elites to change their mindset. With peace and prosperity, the population rose to 400 million, but taxes and government revenues were fixed at a low rate, soon leading to a fiscal crisis. Following China's defeat in the Opium Wars, Western colonial powers forced the Qing government to sign unequal treaties, granting them trading privileges, extraterritoriality and treaty ports under their control. The Taiping Rebellion (1850–1864) and the Dungan Revolt (1862–1877) in western China led to the deaths of over 20 million people, from famine, disease, and war.
The Tongzhi Restoration in the 1860s brought vigorous reforms and the introduction of foreign military technology in the Self-Strengthening Movement. Defeat in the First Sino-Japanese War (1894–1895) led to loss of suzerainty over Korea and cession of Taiwan to the Empire of Japan. The ambitious Hundred Days' Reform in 1898 proposed fundamental change, but was poorly executed and terminated by the Empress Dowager Cixi (1835–1908) in the Wuxu Coup. In 1900, anti-foreign Boxers killed many Chinese Christians and foreign missionaries; in retaliation, the Eight-Nation Alliance invaded China and imposed a punitive indemnity. In response, the government initiated unprecedented fiscal and administrative reforms, including elections, a new legal code, and the abolition of the imperial examination system. Sun Yat-sen and revolutionaries debated reform officials and constitutional monarchists such as Kang Youwei and Liang Qichao over how to transform the Manchu-ruled empire into a modernised Han state. After the deaths of the Guangxu Emperor and Cixi in 1908, Manchu conservatives at court blocked reforms and alienated reformers and local elites alike. The Wuchang Uprising on 10 October 1911 led to the Xinhai Revolution. The abdication of the Xuantong Emperor on 12 February 1912 brought the dynasty to an end.
Names
Hong Taiji proclaimed the Great Qing dynasty in 1636.[18] There are competing explanations as to the meaning of the Chinese character Qīng (清; 'clear', 'pure') in this context. One theory posits a purposeful contrast with the Ming: the character Míng (明; 'bright') is associated with fire within the Chinese zodiacal system, while Qīng (清) is associated with water, illustrating the triumph of the Qing as the conquest of fire by water. The name possibly also possessed Buddhist implications of perspicacity and enlightenment, as well as connection with the bodhisattva Manjusri.[19] Early European writers used the term "Tartar" indiscriminately for all the peoples of Northern Eurasia but in the 17th century Catholic missionary writings established "Tartar" to refer only to the Manchus and "Tartary" for the lands they ruled—i.e. Manchuria and the adjacent parts of Inner Asia,[20][21] as ruled by the Qing before the Ming–Qing transition.
After conquering China proper, the Manchus identified their state as "China", equivalently as Zhōngguó (中國; 'middle kingdom') in Chinese and Dulimbai Gurun in Manchu.[c] The emperors equated the lands of the Qing state (including, among other areas, present-day Northeast China, Xinjiang, Mongolia, and Tibet) as "China" in both the Chinese and Manchu languages, defining China as a multi-ethnic state, and rejecting the idea that only Han areas were properly part of "China". The government used "China" and "Qing" interchangeably to refer to their state in official documents,[22] including the Chinese-language versions of treaties and maps of the world.[23] The term 'Chinese people' (中國人; Zhōngguórén; Manchu: ᡩᡠᠯᡳᠮᠪᠠᡳ
ᡤᡠᡵᡠᠨ ᡳ
ᠨᡳᠶᠠᠯᠮᠠ Dulimbai gurun-i niyalma) referred to all the Han, Manchu, and Mongol subjects of the Qing Empire.[24] When the Qing conquered Dzungaria in 1759, it proclaimed within a Manchu-language memorial that the new land had been absorbed into "China".[25]: 77 The Qing government expounded an ideology that it was bringing the "outer" non-Han peoples—such as various populations of Mongolians, as well as the Tibetans—together with the "inner" Han Chinese into "one family", united within the Qing state. Phraseology like Zhōngwài yījiā (中外一家) and nèiwài yījiā (內外一家)—both translatable as 'home and abroad as one family'—was employed to convey this idea of Qing-mediated trans-cultural unity.[25]: 76–77
History
Formation
The Qing dynasty was founded not by Han Chinese, who constituted a majority of the population, but by Manchus, a sedentary farming people descended from the Jurchens, a Tungusic people who lived in the region now comprising the Chinese provinces of Jilin and Heilongjiang.[26]
Nurhaci
The early form of the Manchu state was founded by Nurhaci, the chieftain of a minor Jurchen tribe – the Aisin-Gioro – in Jianzhou in the early 17th century. Nurhaci may have spent time in a Han household in his youth, and became fluent in Chinese and Mongolian languages and read the Chinese novels Romance of the Three Kingdoms and Water Margin.[27][28] As a vassal of the Ming emperors, he officially considered himself a guardian of the Ming border and a local representative of the Ming dynasty.[16] Nurhaci embarked on an intertribal feud in 1582 that escalated into a campaign to unify the nearby tribes. He also began organizing the Eight Banners military system which included Manchu, Han, and Mongol elements. By 1616, however, he had sufficiently consolidated Jianzhou so as to be able to proclaim himself Khan of the Later Jin dynasty in reference to the previous Jurchen-ruled Jin dynasty.[29]
Two years later, Nurhaci announced the "Seven Grievances" and openly renounced the sovereignty of Ming overlordship in order to complete the unification of those Jurchen tribes still allied with the Ming emperor. After a series of successful battles, he relocated his capital from Hetu Ala to successively bigger captured Ming cities in Liaodong: first Liaoyang in 1621, then Mukden (Shenyang) in 1625.[29] Furthermore, the Khorchin proved a useful ally in the war, lending the Jurchens their expertise as cavalry archers. To guarantee this new alliance, Nurhaci initiated a policy of inter-marriages between the Jurchen and Khorchin nobilities, while those who resisted were met with military action. This is a typical example of Nurhaci's initiatives that eventually became official Qing government policy. During most of the Qing period, the Mongols gave military assistance to the Manchus.[30]
Hong Taiji
Nurhaci died in 1626, and was succeeded by his eighth son, Hong Taiji. Although Hong Taiji was an experienced leader and the commander of two Banners, the Jurchens suffered defeat in 1627, in part due to the Ming's newly acquired Portuguese cannons. To redress the technological and numerical disparity, Hong Taiji in 1634 created his own artillery corps, who cast their own cannons in the European design with the help of defector Chinese metallurgists. One of the defining events of Hong Taiji's reign was the official adoption of the name "Manchu" for the united Jurchen people in November 1635. In 1635, the Manchus' Mongol allies were fully incorporated into a separate Banner hierarchy under direct Manchu command. In April 1636, Mongol nobility of Inner Mongolia, Manchu nobility and the Han mandarin recommended that Hong as the khan of Later Jin should be the emperor of the Great Qing.[31][32] When he was presented with the imperial seal of the Yuan dynasty after the defeat of the last Khagan of the Mongols, Hong Taiji renamed his state from "Great Jin" to "Great Qing" and elevated his position from Khan to Emperor, suggesting imperial ambitions beyond unifying the Manchu territories. Hong Taiji then proceeded to invade Korea again in 1636.
Meanwhile, Hong Taiji set up a rudimentary bureaucratic system based on the Ming model. He established six boards or executive level ministries in 1631 to oversee finance, personnel, rites, military, punishments, and public works. However, these administrative organs had very little role initially, and it was not until the eve of completing the conquest ten years later that they fulfilled their government roles.[33]
Hong Taiji staffed his bureaucracy with many Han Chinese, including newly surrendered Ming officials, but ensured Manchu dominance by an ethnic quota for top appointments. Hong Taiji's reign also saw a fundamental change of policy towards his Han Chinese subjects. Nurhaci had treated Han in Liaodong according to how much grain they had. Due to a Han revolt in 1623, Nurhaci turned against them and enacted discriminatory policies and killings against them. He ordered that Han who assimilated to the Jurchen (in Jilin) before 1619 be treated equally with Jurchens, not like the conquered Han in Liaodong. Hong Taiji recognised the need to attract Han Chinese, explaining to reluctant Manchus why he needed to treat the defecting Ming general Hong Chengchou leniently.[34] Hong Taiji incorporated Han into the Jurchen polity as citizens obligated to provide military service. By 1648, less than one-sixth of the bannermen were of Manchu ancestry.[35]
Claiming the Mandate of Heaven
Hong Taiji died suddenly in September 1643. As Jurchen leaders were chosen by a council of nobles, there was no clear successor. The leading contenders for power were Hong Taiji's oldest son Hooge and Hong Taiji's half brother Dorgon. A compromise installed Hong Taiji's five-year-old son, Fulin, as the Shunzhi Emperor, with Dorgon as regent and de facto leader of the Manchu nation.
Meanwhile, Ming government officials fought against fiscal collapse, against each other, and against a series of peasant rebellions. They were unable to capitalise on the Manchu succession dispute and the resulting boy emperor. In April 1644, Beijing was sacked by a contentious rebel coalition led by Li Zicheng, a former minor Ming official, who established a short-lived Shun dynasty. The last Ming ruler, the Chongzhen Emperor, committed suicide when the city fell to the rebels, marking the effective end of the dynasty.
Li Zicheng then led rebel forces numbering some 200,000 to confront Ming general Wu Sangui, stationed at Shanhai Pass of the Great Wall to defend the capital against the approaching Manchu-led armies. Wu, to survive, had to ally with one of his adversaries against the other; one was a Han Chinese peasant army twice his size, but he chose the other. Wu may have resented Li Zicheng's attack on officials and the social order; Li had taken Wu's father hostage and it was said that Li took Wu's concubine for himself. On the other hand, the Manchus had adopted a Chinese-style form of government and promised stability. Wu and Dorgon allied to defeat Li Zicheng in the Battle of Shanhai Pass on 27 May 1644.[36]
The newly allied armies captured Beijing on 6 June. The Shunzhi Emperor was invested as the "Son of Heaven" on 30 October 1644. The Manchus, who had positioned themselves as political heirs to the Ming, held a formal funeral for the Chongzhen Emperor. However, completing the conquest of China proper took another seventeen years of battling Ming loyalists, pretenders and rebels. The last Ming pretender, Prince Gui, sought refuge with Pindale Min, the king of Burma, but was turned over to a Qing expeditionary army commanded by Wu Sangui, who had him brought back to Yunnan and executed in early 1662.
The Qing had taken shrewd advantage of Ming civilian government discrimination against the military and encouraged the Ming military to defect by spreading the message that the Manchus valued their skills.[37] Banners made up of Han Chinese who defected before 1644 were classed among the Eight Banners, giving them social and legal privileges. Han defectors swelled the ranks of the Eight Banners so greatly that ethnic Manchus became a minority – only 16% in 1648, with Han bannermen dominating at 75% and Mongol bannermen making up the rest.[38] Gunpowder weapons like muskets and artillery were wielded by the Chinese Banners.[39] Normally, Han Chinese defector troops were deployed as the vanguard, while Manchu bannermen were used predominantly for quick strikes with maximum impact, so as to minimise ethnic Manchu losses.[40]
This multi-ethnic force conquered Ming China for the Qing.[41] The three Liaodong officers who played key roles in the conquest of southern China were Shang Kexi, Geng Zhongming, and Kong Youde, who governed southern China autonomously as viceroys for the Qing after the conquest.[42] Han bannermen made up the majority of governors during the early Qing, stabilising their rule.[43] To promote ethnic harmony, a 1648 decree allowed Han Chinese civilian men to marry Manchu women from the Banners with the permission of the Board of Revenue if they were registered daughters of officials or commoners, or with the permission of their banner company captain if they were unregistered commoners. Later in the dynasty the policies allowing intermarriage were done away with.[44] The Qing's depiction of itself as a Chinese empire was not hindered by the imperial house's Manchu ethnicity, especially after 1644, when the name "Chinese" was given a multiethnic meaning.[45]
The first seven years of the young Shunzhi Emperor's reign were dominated by Dorgon's regency. Because of his own political insecurity, Dorgon followed Hong Taiji's example by ruling in the name of the emperor at the expense of rival Manchu princes, many of whom he demoted or imprisoned. Dorgon's precedents and example cast a long shadow. First, the Manchus had entered "South of the Wall" because Dorgon had responded decisively to Wu Sangui's appeal, then, instead of sacking Beijing as the rebels had done, Dorgon insisted, over the protests of other Manchu princes, on making it the dynastic capital and reappointing most Ming officials. No major Chinese dynasty had directly taken over its immediate predecessor's capital, but keeping the Ming capital and bureaucracy intact helped quickly stabilize the regime and sped up the conquest of the rest of the country. Dorgon then drastically reduced the influence of the eunuchs and directed Manchu women not to bind their feet in the Han Chinese style.[46]
However, not all of Dorgon's policies were equally popular or as easy to implement. The controversial July 1645 Queue Order forced adult Han Chinese men to shave the front of their heads and comb the remaining hair into the queue hairstyle which was worn by Manchu men, on pain of death.[47] The popular description of the order was: "To keep the hair, you lose the head; To keep your head, you cut the hair."[46] To the Manchus, this policy was a test of loyalty and an aid in distinguishing friend from foe. For the Han Chinese, however, it was a humiliating reminder of Qing authority that challenged traditional Confucian values.[48] The order triggered strong resistance in Jiangnan.[49] In the ensuing unrest, some 100,000 Han were slaughtered.[50][51][52]
On 31 December 1650, Dorgon died suddenly, marking the start of the Shunzhi Emperor's personal rule. Because the emperor was only 12 years old at that time, most decisions were made on his behalf by his mother, Empress Dowager Xiaozhuang, who turned out to be a skilled political operator. Although his support had been essential to Shunzhi's ascent, Dorgon had centralised so much power in his hands as to become a direct threat to the throne. So much so that upon his death he was bestowed the extraordinary posthumous title of Emperor Yi (義皇帝), the only instance in Qing history in which a Manchu "prince of the blood" (親王) was so honoured. Two months into Shunzhi's personal rule, however, Dorgon was not only stripped of his titles, but his corpse was disinterred and mutilated.[53] Dorgon's fall from grace also led to the purge of his family and associates at court. Shunzhi's promising start was cut short by his early death in 1661 at the age of 24 from smallpox. He was succeeded by his third son Xuanye, who reigned as the Kangxi Emperor.
The Manchus sent Han bannermen to fight against Koxinga's Ming loyalists in Fujian.[54] They removed the population from coastal areas in order to deprive Koxinga's Ming loyalists of resources. This led to a misunderstanding that Manchus were afraid of water. Han bannermen carried out the fighting and killing, casting conquest of the Mingdoubt on the claim that fear of the water led to the coastal evacuation and ban on maritime activities.[55] Even though a poem refers to the soldiers carrying out massacres in Fujian as "barbarians", both Han Green Standard Army and Han bannermen were involved and carried out the worst slaughter.[56] 400,000 Green Standard Army soldiers were used against the Three Feudatories in addition to the 200,000 bannermen.[57]
Kangxi Emperor's reign and consolidation
The 61-year reign of the Kangxi Emperor was the longest of any emperor in Chinese history, and marked the beginning of the High Qing era, the zenith of the dynasty's social, economic and military power. The early Manchu rulers established two foundations of legitimacy that help to explain the stability of their dynasty. The first was the bureaucratic institutions and the neo-Confucian culture that they adopted from earlier dynasties.[58] Manchu rulers and Han Chinese scholar-official elites gradually came to terms with each other. The examination system offered a path for ethnic Han to become officials. Imperial patronage of the Kangxi Dictionary demonstrated respect for Confucian learning, while the Sacred Edict of 1670 effectively extolled Confucian family values. His attempts to discourage Chinese women from foot binding, however, were unsuccessful.
The second major source of stability was the Inner Asian aspect of their Manchu identity, which allowed them to appeal to the Mongol, Tibetan and Muslim subjects.[59] Qing emperors adopted different images for these subjects in their multi-ethnic empire. The Qing used the title of Emperor (Huangdi or hūwangdi),[60] along with Son of Heaven and Ejen in Chinese and Manchu. Like Kublai Khan of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty and Yongle Emperor of the Ming dynasty, Qing rulers like the Qianlong Emperor portrayed the image of themselves as Buddhist sage rulers (wheel-turning kings), patrons of Tibetan Buddhism[61] to maintain legitimacy for Tibetan Buddhists.[62] Mongol subjects also commonly referred to the Qing ruler as Bogda Khan,[63] while Turkic Muslim subjects (now known as the Uyghurs) commonly referred to the Qing ruler as Chinese khagan.[64]
Kangxi's reign began when the young emperor was seven. To prevent a repeat of Dorgon's monopolising of power, on his deathbed his father hastily appointed four regents who were not closely related to the imperial family and had no claim to the throne. However, through chance and machination, Oboi, the most junior of the four, gradually achieved such dominance as to be a potential threat. In 1669, Kangxi disarmed and imprisoned Oboi through trickery – a significant victory for a fifteen-year-old emperor. The young emperor faced challenges in maintaining control of his kingdom, as well. Three Ming generals singled out for their contributions to the establishment of the dynasty had been granted governorships in southern China. They became increasingly autonomous, leading to the Revolt of the Three Feudatories, which lasted for eight years. Kangxi was able to unify his forces for a counterattack led by a new generation of Manchu generals. By 1681, the Qing government had established control over a ravaged southern China, which took several decades to recover.[65]
To extend and consolidate the dynasty's control in Central Asia, the Kangxi Emperor personally led a series of military campaigns against the Dzungars in Outer Mongolia. The Kangxi Emperor expelled Galdan's invading forces from these regions, which were then incorporated into the empire. In 1683, Qing forces received the surrender of Formosa (Taiwan) from Zheng Keshuang, grandson of Koxinga, who had conquered Taiwan from the Dutch colonists as a base against the Qing. Winning Taiwan freed Kangxi's forces for a series of battles over Albazin, the far eastern outpost of the Tsardom of Russia. The 1689 Treaty of Nerchinsk was China's first formal treaty with a European power and kept the border peaceful for the better part of two centuries. Galdan was ultimately killed in the Dzungar–Qing War;[66] after his death, his Tibetan Buddhist followers attempted to control the choice of the next Dalai Lama. Kangxi dispatched two armies to Lhasa, the capital of Tibet, and installed a Dalai Lama sympathetic to the Qing.[67]
Reigns of the Yongzheng and Qianlong emperors
The reigns of the Yongzheng Emperor (r. 1723–1735) and his son, the Qianlong Emperor (r. 1735–1796), marked the height of Qing power. However, the historian Jonathan Spence notes that the empire at the end of Qianlong's reign was "like the sun at midday". Despite "many glories", "signs of decay and even collapse were becoming apparent".[68]
After the death of the Kangxi Emperor in the winter of 1722, his fourth son, Prince Yong (雍親王), became the Yongzheng Emperor. He felt a sense of urgency about the problems that had accumulated in his father's later years.[69] In the words of one recent historian, he was "severe, suspicious, and jealous, but extremely capable and resourceful",[70] and in the words of another, he turned out to be an "early modern state-maker of the first order".[71] First, he promoted Confucian orthodoxy and cracked down on unorthodox sects. In 1723, he outlawed Christianity and expelled most Christian missionaries.[72] He expanded his father's system of Palace Memorials, which brought frank and detailed reports on local conditions directly to the throne without being intercepted by the bureaucracy, and he created a small Grand Council of personal advisors, which eventually grew into the emperor's de facto cabinet for the rest of the dynasty. He shrewdly filled key positions with Manchu and Han Chinese officials who depended on his patronage. When he began to realise the extent of the financial crisis, Yongzheng rejected his father's lenient approach to local elites and enforced collection of the land tax. The increased revenues were to be used for "money to nourish honesty" among local officials and for local irrigation, schools, roads, and charity. Although these reforms were effective in the north, in the south and lower Yangtze valley there were long-established networks of officials and landowners. Yongzheng dispatched experienced Manchu commissioners to penetrate the thickets of falsified land registers and coded account books, but they were met with tricks, passivity, and even violence. The fiscal crisis persisted.[73]
Yongzheng also inherited diplomatic and strategic problems. A team made up entirely of Manchus drew up the 1727 Treaty of Kyakhta to solidify the diplomatic understanding with Russia. In exchange for territory and trading rights, the Qing would have a free hand in dealing with the situation in Mongolia. Yongzheng then turned to that situation, where the Zunghars threatened to re-emerge, and to the southwest, where local Miao chieftains resisted Qing expansion. These campaigns drained the treasury but established the emperor's control of the military and military finance.[74]
When the Yongzheng Emperor died in 1735, his son Prince Bao (寶親王) became the Qianlong Emperor. Qianlong personally led the Ten Great Campaigns to expand military control into present-day Xinjiang and Mongolia, putting down revolts and uprisings in Sichuan and southern China while expanding control over Tibet. The Qianlong Emperor launched several ambitious cultural projects, including the compilation of the Siku Quanshu, the largest collection of books in Chinese history. Nevertheless, Qianlong used the literary inquisition to silence opposition.[75] Beneath outward prosperity and imperial confidence, the later years of Qianlong's reign were marked by rampant corruption and neglect. Heshen, the emperor's handsome young favorite, took advantage of the emperor's indulgence to become one of the most corrupt officials in the history of the dynasty.[76] Qianlong's son, the Jiaqing Emperor (r. 1796–1820), eventually forced Heshen to commit suicide.
Population in the first half of the 17th century did not recover from civil wars and epidemics, but the following years of prosperity and stability led to steady growth. The Qianlong Emperor bemoaned the situation by remarking, "The population continues to grow, but the land does not." The introduction of new crops from the Americas such as the potato and peanut improved nutrition as well, so that the population during the 18th century ballooned from 100 million to 300 million people. Soon farmers were forced to work ever-smaller holdings more intensely.
In 1796, the White Lotus Society raised open rebellion, saying "the officials have forced the people to rebel". Others blamed officials in various parts of the country for corruption, failing to keep the famine relief granaries full, poor maintenance of roads and waterworks, and bureaucratic factionalism. There soon followed uprisings of "new sect" Muslims against local Muslim officials, and Miao tribesmen in southwest China. The White Lotus Rebellion continued until 1804, when badly run, corrupt, and brutal campaigns finally ended it.[77]
Rebellion, unrest, and external pressure
During the early Qing, China continued to be the hegemonic imperial power in East Asia. Although there was no formal ministry of foreign relations, the Lifan Yuan was responsible for relations with the Mongols and Tibetans in Inner Asia, while the tributary system, a loose set of institutions and customs taken over from the Ming, in theory governed relations with East and Southeast Asian countries. The 1689 Treaty of Nerchinsk stabilised relations with the Tsardom of Russia. However, during the 18th century, European empires gradually expanded across the world and developed economies predicated on maritime trade, colonial extraction, and technological advances. The dynasty was confronted with newly developing concepts of the international system and state-to-state relations. European trading posts expanded into territorial control in what is now India and Indonesia. The Qing response was to establish the Canton System in 1756, which restricted maritime trade to Guangzhou and gave monopoly trading rights to private Chinese merchants. This was successful for a time, and the British East India Company and the Dutch East India Company had long before been granted similar monopoly rights by their governments.
In 1793, the British East India Company, with the support of the British government, sent a diplomatic mission to China led by Lord Macartney in order to open trade and put relations on a basis of equality. The imperial court viewed trade as of secondary interest, whereas the British saw maritime trade as the key to their economy. The Qianlong Emperor told Macartney "the kings of the myriad nations come by land and sea with all sorts of precious things", and "consequently there is nothing we lack..."[78]
Since China had little demand for European goods, Europe paid in silver for Chinese goods, an imbalance that worried the mercantilist governments of Britain and France. The growing Chinese demand for opium provided the remedy. The British East India Company greatly expanded its production in Bengal. The Daoguang Emperor, concerned both over the outflow of silver and the damage that opium smoking was causing to his subjects, ordered Lin Zexu to end the opium trade. Lin confiscated the stocks of opium without compensation in 1839, leading Britain to send a military expedition the following year. The First Opium War revealed the outdated state of the Chinese military. The Qing navy, composed entirely of wooden sailing junks, was severely outclassed by the modern tactics and firepower of the British Royal Navy. British soldiers, using advanced muskets and artillery, easily outmaneuvered and outgunned Qing forces in ground battles. The Qing surrender in 1842 marked a decisive, humiliating blow. The Treaty of Nanjing, the first of the "unequal treaties", demanded war reparations, forced China to open up the Treaty Ports of Canton, Amoy, Fuzhou, Ningbo and Shanghai to Western trade and missionaries, and to cede Hong Kong Island to Britain. It revealed weaknesses in the Qing government and provoked rebellions against the regime.
The Taiping Rebellion (1849–1864) was the first major anti-Manchu movement. Amid widespread social unrest and worsening famine, the rebellion not only posed the most serious threat to Qing rule, but during its 14-year course, between 20 and 30 million people died.[79] The rebellion began under the leadership of Hong Xiuquan (1814–1864), a disappointed civil service examination candidate who, influenced by reading the Old Testament in translation, had a series of visions and announced himself to be the son of God, the younger brother of Jesus Christ, sent to reform China.[80] In 1851, Hong launched an uprising in Guizhou and established the Taiping Heavenly Kingdom with himself as its king. Within this kingdom, slavery, concubinage, arranged marriage, opium smoking, footbinding, judicial torture, and the worship of idols were all banned. However, success led to internal feuds, defections and corruption. In addition, British and French troops, equipped with modern weapons, had come to the assistance of the Qing army. Nonetheless, it was not until 1864 that Qing forces under Zeng Guofan succeeded in crushing the revolt. After the outbreak of this rebellion, there were also revolts by the Muslims and Miao people of China against the Qing, most notably in the Miao Rebellion (1854–1873) in Guizhou, the Panthay Rebellion (1856–1873) in Yunnan, and the Dungan Revolt (1862–1877) in the northwest.
The Western powers, largely unsatisfied with the Treaty of Nanjing, gave grudging support to the Qing government during the Taiping and Nian rebellions. China's income fell sharply during the wars as vast areas of farmland were destroyed, millions of lives were lost, and countless armies were raised and equipped to fight the rebels. In 1854, Britain tried to re-negotiate the Treaty of Nanjing, inserting clauses allowing British commercial access to Chinese rivers and the creation of a permanent British embassy at Beijing.
In 1856, Qing authorities, in searching for a pirate, boarded a ship, the Arrow, which the British claimed had been flying the British flag, an incident which led to the Second Opium War. In 1858, facing no other options, the Xianfeng Emperor agreed to the Treaty of Tientsin, which contained clauses deeply insulting to the Chinese, such as a demand that all official Chinese documents be written in English and a proviso granting British warships unlimited access to all navigable Chinese rivers.
Ratification of the treaty in the following year led to a resumption of hostilities. In 1860, with Anglo-French forces marching on Beijing, the emperor and his court fled the capital for the imperial hunting lodge at Rehe. Once in Beijing, the Anglo-French forces looted and burned the Old Summer Palace and, in an act of revenge for the arrest, torture, and execution of the English diplomatic mission.[81] Prince Gong, a younger half-brother of the emperor, who had been left as his brother's proxy in the capital, was forced to sign the Convention of Beijing. The humiliated emperor died the following year at Rehe.
Self-strengthening and frustration of reforms
Following the death of the Xianfeng Emperor in 1861, and the accession of the 5-year-old Tongzhi Emperor, the Qing rallied. In the Tongzhi Restoration, Han Chinese officials such as Zuo Zongtang stood behind the Manchus and organised provincial troops. Zeng Guofan, in alliance with Prince Gong, sponsored the rise of younger officials such as Li Hongzhang, who put the dynasty back on its feet financially and instituted the Self-Strengthening Movement, which adopted Western military technology in order to preserve Confucian values.Their institutional reforms included China's first unified ministry of foreign affairs in the Zongli Yamen, allowing foreign diplomats to reside in the capital, the establishment of the Imperial Maritime Customs Service, the institution of modern navy and army forces including the Beiyang Army, and the purchase of armament factories from the Europeans.[82]
The dynasty gradually lost control of its peripheral territories. In return for promises of support against the British and the French, the Russian Empire took large chunks of territory in the Northeast in 1860. The period of cooperation between the reformers and the European powers ended with the 1870 Tianjin Massacre, which was incited by the murder of French nuns set off by the belligerence of local French diplomats. Starting with the Cochinchina Campaign in 1858, France expanded control of Indochina. By 1883, France was in full control of the region and had reached the Chinese border. The Sino-French War began with a surprise attack by the French on the Chinese southern fleet at Fuzhou. After that the Chinese declared war on the French. A French invasion of Taiwan was halted and the French were defeated on land in Tonkin at the Battle of Bang Bo. However Japan threatened to enter the war against China due to the Gapsin Coup and China chose to end the war with negotiations. The war ended in 1885 with the Treaty of Tientsin and the Chinese recognition of the French protectorate in Vietnam.[83] Some Russian and Chinese gold miners also established a short-lived proto-state known as the Zheltuga Republic (1883–1886) in the Amur River basin, which was however soon crushed by the Qing forces.[84]
In 1884, Qing China obtained concessions in Korea, such as the Chinese concession of Incheon,[85] but the pro-Japanese Koreans in Seoul led the Gapsin Coup. Tensions between China and Japan rose after China intervened to suppress the uprising. The Japanese prime minister Itō Hirobumi and Li Hongzhang signed the Convention of Tientsin, an agreement to withdraw troops simultaneously, but the First Sino-Japanese War of 1895 was a military humiliation. The Treaty of Shimonoseki recognised Korean independence and ceded Taiwan and the Pescadores to Japan. The terms might have been harsher, but when a Japanese citizen attacked and wounded Li Hongzhang, an international outcry shamed the Japanese into revising them. The original agreement stipulated the cession of Liaodong Peninsula to Japan, but Russia, with its own designs on the territory, along with Germany and France, in the Triple Intervention, successfully put pressure on the Japanese to abandon the peninsula.
These years saw the participation of Empress Dowager Cixi in state affairs. Cixi initially entered the imperial palace in the 1850s as a concubine of the Xianfeng Emperor, and became the mother of the future Tongzhi Emperor. Following the his accession at the age of five, Cixi, Xianfeng's widow Empress Dowager Ci'an, and Prince Gong (a son of the Daoguang Emperor), staged a coup that ousted several of the Tongzhi Emperor's regents. Between 1861 and 1873, Cixi and Ci'an served as regents together; following the emperor's death in 1875, Cixi's nephew, the Guangxu Emperor, took the throne in violation of the custom that the new emperor be of the next generation, and another regency began. Ci'an suddenly died in the spring of 1881, leaving Cixi as sole regent.[86]
From 1889, when Guangxu began to rule in his own right, until 1898, the Empress Dowager lived in semi-retirement, spending the majority of the year at the Summer Palace. In 1897, two German Roman Catholic missionaries were murdered in southern Shandong province (the Juye Incident). Germany used the murders as a pretext for a naval occupation of Jiaozhou Bay. The occupation prompted a Scramble for China in 1898, which included the German lease of Jiaozhou Bay, the Russian lease of Liaodong, the British lease of the New Territories of Hong Kong, and the French lease of Guangzhouwan.
In the wake of these external defeats, the Guangxu Emperor initiated the Hundred Days' Reform in 1898. Newer, more radical advisers such as Kang Youwei were given positions of influence. The emperor issued a series of edicts and plans were made to reorganise the bureaucracy, restructure the school system, and appoint new officials. Opposition from the bureaucracy was immediate and intense. Although she had been involved in the initial reforms, the Empress Dowager stepped in to call them off, arrested and executed several reformers, and took over day-to-day control of policy. Yet many of the plans stayed in place, and the goals of reform were implanted.[87]
Drought in North China, combined with the imperialist designs of European powers and the instability of the Qing government, created background conditions for the Boxers. In 1900, local groups of Boxers proclaiming support for the Qing dynasty murdered foreign missionaries and large numbers of Chinese Christians, then converged on Beijing to besiege the Foreign Legation Quarter. A coalition of European, Japanese, and Russian armies (the Eight-Nation Alliance) then entered China without diplomatic notice, much less permission. Cixi declared war on all of these nations, only to lose control of Beijing after a short, but hard-fought campaign. She fled to Xi'an. The victorious allies then enforced their demands on the Qing government, including compensation for their expenses in invading China and execution of complicit officials, via the Boxer Protocol.[88]
Reform, revolution, collapse
The defeat by Japan in 1895 created a sense of crisis which the failure of the 1898 reforms and the disasters of 1900 only exacerbated. Cixi in 1901 moved to mollify the foreign community, called for reform proposals, and initiated the Late Qing reforms. Over the next few years the reforms included the restructuring of the national education, judicial, and fiscal systems, the most dramatic of which was the abolition of the imperial examination system in 1905.[89] The court directed a constitution to be drafted, and provincial elections were held, the first in China's history.[90] Sun Yat-sen and revolutionaries debated reform officials and constitutional monarchists such as Kang Youwei and Liang Qichao over how to transform the Manchu-ruled empire into a modernised Han Chinese state.[91]
The Guangxu Emperor died on 14 November 1908, and Cixi died the following day. Puyi, the oldest son of Zaifeng, Prince Chun, and nephew to the childless Guangxu Emperor, was appointed successor at the age of two, leaving Zaifeng with the regency. Zaifeng forced Yuan Shikai to resign. The Qing dynasty became a constitutional monarchy on 8 May 1911, when Zaifeng created a "responsible cabinet" led by Yikuang, Prince Qing. However, it became known as the "royal cabinet", as five of its thirteen members, were part of or related to the royal family.[92]
The Wuchang Uprising on 10 October 1911 set off a series of uprisings. By November, 14 of the 22 provinces had rejected Qing rule. This led to the creation of the Republic of China, in Nanjing on 1 January 1912, with Sun Yat-sen as its provisional head. Seeing a desperate situation, the Qing court brought Yuan Shikai back to power. His Beiyang Army crushed the revolutionaries in Wuhan at the Battle of Yangxia. After taking the position of Prime Minister he created his own cabinet, with the support of Empress Dowager Longyu. However, Yuan Shikai decided to cooperate with Sun Yat-sen's revolutionaries to overthrow the Qing dynasty.
On 12 February 1912, Longyu issued the abdication of the child emperor Puyi leading to the fall of the Qing dynasty under the pressure of Yuan Shikai's Beiyang army despite objections from conservatives and royalist reformers.[93] This brought an end to over 2,000 years imperial governance in China, and began a period of instability. In July 1917, there was an abortive attempt to restore the Qing led by Zhang Xun. Puyi was allowed to live in the Forbidden City after his abdication until 1924, when he moved to the Japanese concession in Tianjin. The Empire of Japan invaded Northeast China and founded Manchukuo there in 1932, with Puyi as its emperor. After the invasion of Northeast China to fight Japan by the Soviet Union, Manchukuo fell in 1945.
Government
The early Qing emperors adopted the bureaucratic structures and institutions from the Ming, but split rule between Han and Manchus, with some positions also given to Mongols.[94] Like previous dynasties, the Qing recruited officials via the imperial examination system, until the system was abolished in 1905. The Qing divided the positions into civil and military positions, each having nine grades or ranks, each subdivided into a and b categories. Civil appointments ranged from an attendant to the emperor or a Grand Secretary in the Forbidden City (highest) to being a prefectural tax collector, deputy jail warden, deputy police commissioner, or tax examiner. Military appointments ranged from being a field marshal or chamberlain of the imperial bodyguard to a third class sergeant, corporal or a first or second class private.[95]
While the Qing dynasty tried to maintain the traditional tributary system of China, by the 19th century Qing China had become part of a European-style community of sovereign states[96] and established official diplomatic relations with more than twenty countries around the world before its downfall, and since the 1870s it established legations and consulates.
Central government agencies
The formal structure of the Qing government centred on the Emperor as the absolute ruler, who presided over six Boards (Ministries[d]), each headed by two presidents[e] and assisted by four vice presidents.[f] In contrast to the Ming system, however, Qing ethnic policy dictated that appointments were split between Manchu noblemen and Han officials who had passed the highest levels of the state examinations. The Grand Secretariat,[g] which had been an important policy-making body under the Ming, lost its importance during the Qing and evolved into an imperial chancery. The institutions which had been inherited from the Ming formed the core of the Qing "Outer Court", which handled routine matters and was located in the southern part of the Forbidden City.[97]
In order not to let the routine administration take over the running of the empire, the Qing emperors made sure that all important matters were decided in the "Inner Court", which was dominated by the imperial family and Manchu nobility and which was located in the northern part of the Forbidden City. The core institution of the inner court was the Grand Council.[h] It emerged in the 1720s under the reign of the Yongzheng Emperor as a body charged with handling Qing military campaigns against the Mongols, but soon took over other military and administrative duties, centralising authority under the crown.[98] The Grand Councillors[i] served as a sort of privy council to the emperor.
From the early Qing, the central government was characterised by a system of dual appointments by which each position in the central government had a Manchu and a Han Chinese assigned to it. The Han Chinese appointee was required to do the substantive work and the Manchu to ensure Han loyalty to Qing rule.[99] While the Qing government was established as an absolute monarchy like previous dynasties in China, by the early 20th century however the Qing court began to move towards a constitutional monarchy,[100] with government bodies like the Advisory Council established and a parliamentary election to prepare for a constitutional government.[101][102]
There was also another government institution called Imperial Household Department which was unique to the Qing dynasty. It was established before the fall of the Ming, but it became mature only after 1661, following the death of the Shunzhi Emperor and the accession of his son, the Kangxi Emperor.[103] The department's original purpose was to manage the internal affairs of the imperial family and the activities of the inner palace (in which tasks it largely replaced eunuchs), but it also played an important role in Qing relations with Tibet and Mongolia, engaged in trading activities (jade, ginseng, salt, furs, etc.), managed textile factories in the Jiangnan region, and even published books.[104] Relations with the Salt Superintendents and salt merchants, such as those at Yangzhou, were particularly lucrative, especially since they were direct, and did not go through absorptive layers of bureaucracy. The department was manned by booi,[j] or "bondservants", from the Upper Three Banners.[105] By the 19th century, it managed the activities of at least 56 subagencies.[103][106]
Military
The Qing dynasty was established by conquest and maintained by armed force. The founding emperors personally organised and led the armies, and the continued cultural and political legitimacy of the dynasty depended on the ability to defend the country from invasion and expand its territory. Therefore, military institutions, leadership, and finance were fundamental to the dynasty's initial success and ultimate decay. The early military system centred on the Eight Banners, a hybrid institution that also played social, economic, and political roles.[107] The Banner system was developed on an informal basis as early as 1601, and formally established in 1615 by Jurchen leader Nurhaci (1559–1626), the retrospectively recognised founder of the Qing. His son Hong Taiji (1592–1643), who renamed the Jurchens "Manchus," created eight Mongol banners to mirror the Manchu ones and eight "Han-martial" (??; Hànjun) banners manned by Chinese who surrendered to the Qing before the full-fledged conquest of China proper began in 1644. After 1644, the Ming Chinese troops that surrendered to the Qing were integrated into the Green Standard Army, a corps that eventually outnumbered the Banners by three to one.
The use of gunpowder during the High Qing can compete with the three gunpowder empires in western Asia.[108] Manchu imperial princes led the Banners in defeating the Ming armies, but after lasting peace was established starting in 1683, both the Banners and the Green Standard Armies started to lose their efficiency. Garrisoned in cities, soldiers had few occasions to drill. The Qing nonetheless used superior armament and logistics to expand deeply into Central Asia, defeat the Dzungar Mongols in 1759, and complete their conquest of Xinjiang. Despite the dynasty's pride in the Ten Great Campaigns of the Qianlong Emperor (r. 1735–1796), the Qing armies became largely ineffective by the end of the 18th century. It took almost ten years and huge financial waste to defeat the badly equipped White Lotus Rebellion (1795–1804), partly by legitimizing militias led by local Han Chinese elites. The Taiping Rebellion (1850–1864), a large-scale uprising that started in southern China, marched within miles of Beijing in 1853. The Qing court was forced to let its Han Chinese governors-general, first led by Zeng Guofan, raise regional armies. This new type of army and leadership defeated the rebels but signaled the end of Manchu dominance of the military establishment.
The military technology of the European Industrial Revolution made China's armament and military rapidly obsolete. In 1860 British and French forces in the Second Opium War captured Beijing and sacked the Summer Palace. The shaken court attempted to modernise its military and industrial institutions by buying European technology. This Self-Strengthening Movement established shipyards (notably the Jiangnan Arsenal and the Foochow Arsenal) and bought modern guns and battleships in Europe. The Qing navy became the largest in East Asia. But organisation and logistics were inadequate, officer training was deficient, and corruption widespread. The Beiyang Fleet was virtually destroyed and the modernised ground forces defeated in the 1895 First Sino-Japanese War. The Qing created a New Army, but could not prevent the Eight Nation Alliance from invading China to put down the Boxer Uprising in 1900. The revolt of a New Army corps in 1911 led to the fall of the dynasty.
Administrative divisions
The Qing reached its largest extent during the 18th century, when it ruled China proper (eighteen provinces) as well as the areas of present-day Northeast China, Inner Mongolia, Outer Mongolia, Xinjiang and Tibet, at approximately 13,000,000 km2 (5,000,000 sq mi) in size. There were originally 18 provinces, all in China proper, but this number was later increased to 22, with Manchuria and Xinjiang being divided or turned into provinces. Taiwan, originally part of Fujian, became a province of its own in the 19th century,[109] but was ceded to Japan following the First Sino-Japanese War in 1895.[110]
Territorial administration
This section needs additional citations for verification. (March 2022) |
The Qing organisation of provinces was based on the fifteen administrative units set up by the Ming dynasty, later made into eighteen provinces by splitting for example, Huguang into Hubei and Hunan provinces. The provincial bureaucracy continued the Yuan and Ming practice of three parallel lines, civil, military, and censorate, or surveillance. Each province was administered by a governor and a provincial military commander. Below the province were prefectures operating under a prefect, followed by subprefectures under a subprefect. The lowest unit was the county, overseen by a county magistrate. The eighteen provinces are also known as "China proper". The position of viceroy was the highest rank in the provincial administration. There were eight regional viceroys in China proper, each usually took charge of two or three provinces. The Viceroy of Zhili, who was responsible for the area surrounding Beijing, is usually considered as the most honourable and powerful viceroy among the eight.
By the mid-18th century, the Qing had successfully put outer regions under its control. Imperial commissioners and garrisons were sent to Mongolia and Tibet to oversee their affairs. These territories were also under supervision of a central government institution called Lifan Yuan. Qinghai was also put under direct control of the Qing court. Xinjiang, also known as Chinese Turkestan, was subdivided into the regions north and south of the Tian Shan mountains, also known today as Dzungaria and Tarim Basin respectively, but the post of Ili General was established in 1762 to exercise unified military and administrative jurisdiction over both regions. Dzungaria was fully opened to Han migration by the Qianlong Emperor from the beginning. Han migrants were at first forbidden from permanently settling in the Tarim Basin but were the ban was lifted after the invasion by Jahangir Khoja in the 1820s. Likewise, Manchuria was also governed by military generals until its division into provinces, though some areas of Xinjiang and Northeast China were lost to the Russian Empire in the mid-19th century. Manchuria was originally separated from China proper by the Inner Willow Palisade, a ditch and embankment planted with willows intended to restrict the movement of the Han Chinese, as the area was off-limits to civilian Han Chinese until the government started colonising the area, especially since the 1860s.
With respect to these outer regions, the Qing maintained imperial control, with the emperor acting as Mongol khan, patron of Tibetan Buddhism and protector of Muslims. However, Qing policy changed with the establishment of Xinjiang province in 1884. During the Great Game, taking advantage of the Dungan revolt in northwest China, Yakub Beg invaded Xinjiang from Central Asia with support from the British Empire, and made himself the ruler of the kingdom of Kashgaria. The Qing court sent forces to defeat Yaqub Beg and Xinjiang was reconquered, and then the political system of China proper was formally applied onto Xinjiang. The Kumul Khanate, which was incorporated into the Qing dynasty as a vassal after helping Qing defeat the Zunghars in 1757, maintained its status after Xinjiang turned into a province through the end of the dynasty in the Xinhai Revolution up until 1930.[111] In the early 20th century, Britain sent an expedition force to Tibet and forced Tibetans to sign a treaty. The Qing court responded by asserting Chinese sovereignty over Tibet,[112] resulting in the 1906 Anglo-Chinese Convention signed between Britain and China. The British agreed not to annex Tibetan territory or to interfere in the administration of Tibet, while China engaged not to permit any other foreign state to interfere with the territory or internal administration of Tibet.[113] The Qing government also turned Manchuria into three provinces in the early 20th century, officially known as the "Three Northeast Provinces", and established the post of Viceroy of the Three Northeast Provinces to oversee these provinces.
Society
Population growth and mobility
The population grew in numbers, density, and mobility. The population in 1700 was roughly 150 million, about what it had been a century before, then doubled over the next century, and reached a height of 450 million on the eve of the Taiping Rebellion in 1850.[114] The spread of New World crops, such as maize, peanuts, sweet potatoes, and potatoes decreased the number of deaths from malnutrition. Diseases such as smallpox were brought under control by an increase in inoculations. In addition, infant deaths were decreased due to campaigns against infanticide and improvements in birthing techniques performed by doctors and midwives and an increase in medical books available to the public.[115] European population growth in this period was greatest in the cities, but in China there was only slow growth in cities and the lower Yangzi. The greatest growth was in the borderlands and the highlands, where farmers moved to take advantage of large tracts of marshlands and forests.[116]
The population was remarkably mobile, perhaps more so than at any time in Chinese history. Millions of Han Chinese migrated to Yunnan and Guizhou in the 18th century, and also to Taiwan. After the conquests of the 1750s and 1760s, the court organised agricultural colonies in Xinjiang. This mobility also included the privately organised movement of Qing subjects overseas, largely to Southeast Asia, to pursue trade and other economic opportunities.[116]
Manchuria, however, was formally closed to Han settlement by the Willow Palisade, with the exception of some bannermen.[117] Nonetheless, by 1780, Han Chinese had become 80% of the population.[118] The relatively sparse populatikon made the territory vulnerable to Russian annexation. In response, the Qing officials proposed in 1860 to open parts of Guandong to Chinese civilian farmer settlers.[119] Late 19th century Manchuria was opened up to Han settlers, resulting in more extensive migration.[120] By the dawn of the 20th century, largely in an attempt to counteract increasing Russian influence, the Qing had abolished the existing administrative system in Manchuria, reclassified all immigrants to the region as "Han" instead of "civilians", and replaced provincial generals with provincial governors. From 1902 to 1911, 70 civil administrations were created in Manchuria, owing to the region's growing population.[121]
Social status
According to statute, Qing society was divided into relatively closed estates, of which in most general terms there were five. Apart from the estates of the officials, the comparatively minuscule aristocracy, and the degree-holding scholar-officials, there also existed a major division among ordinary Chinese between commoners and people with inferior status.[122] They were divided into two categories: one of them, the good "commoner" people, the other "mean" people who were seen as debased and servile. The majority of the population belonged to the first category and were described as liangmin, a legal term meaning good people, as opposed to jianmin meaning the mean (or ignoble) people. Qing law explicitly stated that the traditional four occupations (scholars, farmers, artisans and merchants) were "good", or having a status of commoners. On the other hand, slaves or bondservants, entertainers (including prostitutes and actors), tattooed criminals, and those low-level employees of government officials were the "mean people". Mean people were legally inferior to commoners and suffered unequal treatments, such as being forbidden to take the imperial examination.[123] Furthermore, such people were usually not allowed to marry with free commoners and were even often required to acknowledge their abasement in society through actions such as bowing. However, throughout the Qing dynasty, the emperor and his court, as well as the bureaucracy, worked towards reducing the distinctions between the debased and free but did not completely succeed even at the end of its era in merging the two classifications together.[124]
Qing gentry
Although there had been no powerful hereditary aristocracy since the Song dynasty, the gentry, like their British counterparts, enjoyed imperial privileges and managed local affairs. The status of scholar-officials was defined by passing at least the first level of civil service examinations and holding a degree, which qualified him to hold imperial office, although he might not actually do so. The gentry member could legally wear gentry robes and could talk to officials as equals. Informally, the gentry then presided over local society and could use their connections to influence the magistrate, acquire land, and maintain large households. The gentry thus included not only males holding degrees but also their wives and some of their relatives.[125]
The gentry class was divided into groups. Not all who held office were literati, as merchant families could purchase degrees, and not all who passed the exams found employment as officials, since the number of degree-holders was greater than the number of openings. The gentry class also differed in the source and amount of their income. Literati families drew income from landholding, as well as from lending money. Officials drew a salary, which, as the years went by, were less and less adequate, leading to widespread reliance on "squeeze", irregular payments. Those who prepared for but failed the exams, like those who passed but were not appointed to office, could become tutors or teachers, private secretaries to sitting officials, administrators of guilds or temples, or other positions that required literacy. Others turned to fields such as engineering, medicine, or law, which by the nineteenth century demanded specialised learning. By the nineteenth century, it was no longer shameful to become an author or publisher of fiction.[126]
The Qing gentry were marked as much by their aspiration to a cultured lifestyle as by their legal status. They lived more refined and comfortable lives than the commoners and used sedan-chairs to travel any significant distance. They often showed off their learning by collecting objects such as scholars' stones, porcelain or pieces of art for their beauty, which set them off from less cultivated commoners.[127]
Qing nobility
Family and kinship
During the Qing, the building block of society was patrilineal kinship. A shift in marital practices, identity and loyalty had begun during the Song, when the civil service examination began to replace nobility and inheritance as a means for gaining status. Instead of intermarrying within aristocratic elites of the same social status, they tended to form marital alliances with nearby families of the same or higher wealth, and established the local people's interests as first and foremost which helped to form intermarried townships.[128] The neo-Confucian ideology, especially the Cheng-Zhu thinking favored by Qing social thought, emphasised patrilineal families and genealogy in society.[129]
The emperors and local officials exhorted families to compile genealogies in order to stabilise local society.[130] The genealogy was placed in the ancestral hall, which served as the lineage's headquarters and a place for annual ancestral sacrifice. A specific Chinese character appeared in the given name of each male of each generation, often well into the future. These lineages claimed to be based on biological descent but when a member of a lineage gained office or became wealthy, he might use considerable creativity in selecting a prestigious figure to be "founding ancestor".[131] Such worship was intended to ensure that the ancestors remain content and benevolent spirits (shen) who would keep watch over and protect the family. Later observers felt that the ancestral cult focused on the family and lineage, rather than on more public matters such as community and nation.[132]
Inner Mongols and Khalkha Mongols in the Qing rarely knew their ancestors beyond four generations and Mongol tribal society was not organised among patrilineal clans, contrary to what was commonly thought, but included unrelated people at the base unit of organisation.[133] The Qing tried but failed to promote the Chinese Neo-Confucian ideology of organising society along patrimonial clans among the Mongols.[134]
Religion
Manchu rulers presided over a multi-ethnic empire and the emperor, who was held responsible for "all under heaven", patronised and took responsibility for all religions and belief systems. The empire's "spiritual centre of gravity" was the "religio-political state".[135] Since the empire was part of the order of the cosmos, which conferred the Mandate of Heaven, the emperor as "Son of Heaven" was both the head of the political system and the head priest of the State Cult. The emperor and his officials, who were his personal representatives, took responsibility over all aspects of the empire, especially spiritual life and religious institutions and practices.[136] The county magistrate, as the emperor's political and spiritual representative, made offerings at officially recognised temples. The magistrate lectured on the Emperor's Sacred Edict to promote civic morality; he kept close watch over religious organisations whose actions might threaten the sovereignty and religious prerogative of the state.[137]
Manchu and imperial religion
The Manchu imperial family were especially attracted by Yellow Sect or Gelug Buddhism that had spread from Tibet into Mongolia. The Fifth Dalai Lama, who had gained power in 1642, just before the Manchus took Beijing, looked to the Qing court for support. The Kangxi and Qianlong emperors practiced this form of Tibetan Buddhism as one of their household religions and built temples that made Beijing one of its centres, and constructed a replica Lhasa's Potala Palace at their summer retreat in Rehe.[138]
Shamanism, the most common religion among Manchus, was a spiritual inheritance from their Tungusic ancestors that set them off from Han Chinese.[139] State shamanism was important to the imperial family both to maintain their Manchu cultural identity and to promote their imperial legitimacy among tribes in the northeast.[140] Imperial obligations included rituals on the first day of Chinese New Year at a shamanic shrine (tangse).[141] Practices in Manchu families included sacrifices to the ancestors, and the use of shamans, often women, who went into a trance to seek healing or exorcism.[142]
Popular religion
Chinese folk religion was centred around the patriarchal family and shen, or spirits. Common practices included ancestor veneration, filial piety, local gods and spirits. Rites included mourning, funeral, burial, practices.[143] Since they did not require exclusive allegiance, forms and branches of Confucianism, Buddhism, and Daoism were intertwined, for instance in the syncretic Three teachings.[144] Chinese folk religion combined elements of the three, with local variations.[145] County magistrates, who were graded and promoted on their ability to maintain local order, tolerated local sects and even patronised local temples as long as they were orderly, but were suspicious of heterodox sects that defied state authority and rejected imperial doctrines. Some of these sects indeed had long histories of rebellion, such as the Way of Former Heaven, which drew on Daoism, and the White Lotus Society, which drew on millennial Buddhism. The White Lotus Rebellion (1796–1804) confirmed official suspicions as did the Taiping Rebellion, which drew on millennial Christianity.
Christianity, Judaism, and Islam
The Abrahamic religions had arrived from Western Asia as early as the Tang dynasty but their insistence that they should be practised to the exclusion of other religions made them less adaptable than Buddhism, which had quickly been accepted as native. Islam predominated in Central Asian areas of the empire, while Judaism and Christianity were practiced in well-established but self-contained communities.[146]
Several hundred Catholic missionaries arrived between the late Ming period and the proscription of Christianity in 1724. The Jesuits adapted to Chinese expectations, evangelised among the educated, adopted the robes and lifestyles of literati, became proficient in the Confucian classics, and did not challenge Chinese moral values. They proved their value to the early Manchu emperors with their work in gunnery, cartography, and astronomy, but fell out of favor for a time until the Kangxi Emperor's 1692 edict of toleration.[147] In the countryside, the newly arrived Dominican and Franciscan clerics established rural communities that adapted to local folk religious practices by emphasising healing, festivals, and holy days rather than sacraments and doctrine.[148] In 1724, the Yongzheng Emperor proscribed Christianity as a "heterodox teaching". [149] Since the European Catholic missionaries had kept control in their own hands and had not allowed the creation of a native clergy, however, the number of Catholics would grow more rapidly after 1724 because local communities could now set their own rules and standards. In 1811, Christian religious activities were further criminalised by the Jiaqing Emperor.[150] The imperial ban was lifted by Treaty in 1846.[151]
The first Protestant missionary to China, Robert Morrison (1782–1834) of the London Missionary Society (LMS), arrived at Canton on 6 September 1807. [152] He completed a translation of the entire Bible in 1819.[153] Liang Afa (1789–1855), a Morrison-trained Chinese convert, extended evangelisation into inner China.[154][155] The two Opium Wars (1839–1860) marked the watershed of Protestant Christian missions. The series of treaties signed between the 1842 Treaty of Nanjing and the 1858 Treaty of Tianjin distinguished Christianity from local religions and granted it protected status.[156]
In the late 1840s Hong Xiuquan read Morrison's Chinese Bible, as well as Liang Afa's evangelistic pamphlet, and announced to his followers that Christianity in fact had been the religion of ancient China before Confucius and his followers drove it out.[157] He formed the Taiping Movement, which emerged in South China as a "collusion of the Chinese tradition of millenarian rebellion and Christian messianism", "apocalyptic revolution, Christianity, and 'communist utopianism'".[158]
After 1860, enforcement of the treaties allowed missionaries to spread their evangelisation efforts outside Treaty Ports. Their presence created cultural and political opposition. Historian John K. Fairbank observed that "[t]o the scholar-gentry, Christian missionaries were foreign subversives, whose immoral conduct and teaching were backed by gunboats".[159] In the next decades, there were some 800 conflicts between village Christians and non-Christians mostly about non-religious issues, such as land rights or local taxes, but religious conflict often lay behind such cases.[160] In the summer of 1900, as foreign powers contemplated the division of China, village youths, known as Boxers, who practiced Chinese martial arts and spiritual practices, attacked and murdered Chinese Christians and foreign missionaries in the Boxer Uprising. The imperialist powers once again invaded and imposed a substantial indemnity. This defeat convinced many among the educated elites that popular religion was an obstacle to China's development as a modern nation, and some turned to Christianity as a spiritual tool to build one.[161]
By 1900, there were about 1,400 Catholic priests and nuns in China serving nearly 1 million Catholics. Over 3,000 Protestant missionaries were active among the 250,000 Protestant Christians in China.[162] Western medical missionaries established clinics and hospitals, and led medical training in China.[163] Missionaries began establishing nurse training schools in the late 1880s, but nursing of sick men by women was rejected by local tradition, so the number of students was small until the 1930s.[164]
Economy
By the end of the 17th century, the Chinese economy had recovered from the devastation caused by the wars in which the Ming dynasty were overthrown.[165] In the following century, markets continued to expand, but with more trade between regions, a greater dependence on overseas markets and a greatly increased population.[166] By the end of the 18th century the population had risen to 300 million from approximately 150 million during the late Ming dynasty. The dramatic rise in population was due to several reasons, including the long period of peace and stability in the 18th century and the import of new crops China received from the Americas, including peanuts, sweet potatoes and maize. New species of rice from Southeast Asia led to a huge increase in production. Merchant guilds proliferated in all of the growing Chinese cities and often acquired great social and even political influence. Rich merchants with official connections built up huge fortunes and patronised literature, theater and the arts. Textile and handicraft production boomed.[167]
The government broadened land ownership by returning land that had been sold to large landowners in the late Ming period by families unable to pay the land tax.[168] To give people more incentives to participate in the market, they reduced the tax burden in comparison with the late Ming, and replaced the corvée system with a head tax used to hire laborers.[169] The administration of the Grand Canal was made more efficient, and transport opened to private merchants.[170] A system of monitoring grain prices eliminated severe shortages, and enabled the price of rice to rise slowly and smoothly through the 18th century.[171] Wary of the power of wealthy merchants, Qing rulers limited their trading licenses and usually refused them permission to open new mines, except in poor areas.[172] These restrictions on domestic resource exploration, as well as on foreign trade, are critiqued by some scholars as a cause of the Great Divergence, by which the West overtook China economically.[173][174]
During the Ming–Qing period (1368–1911) the biggest development in the Chinese economy was its transition from a command to a market economy, the latter becoming increasingly more pervasive throughout the Qing's rule.[132] Between roughly 1550 and 1800, China proper experienced a second commercial revolution, developing naturally from the first commercial revolution during the Song, which saw the emergence of long-distance inter-regional trade of luxury goods. During the second commercial revolution, for the first time, a large percentage of farming households began producing crops for sale in the local and national markets rather than for their own consumption or barter in the traditional economy. Surplus crops were placed onto the national market for sale, integrating farmers into the commercial economy from the ground up. This naturally led to regions specialising in certain cash-crops for export as China's economy became increasingly reliant on inter-regional trade of bulk staple goods such as cotton, grain, beans, vegetable oils, forest products, animal products, and fertiliser.[124]
Silver
Silver entered in large quantities from mines in the New World after the Spanish conquered the Philippines in the 1570s. The re-opening of the southeast coast, which had been closed in the late 17th century, quickly revived trade, which expanded at 4% per annum throughout the latter part of the 18th century.[175] China continued to export tea, silk and manufactures, creating a large, favorable trade balance with the West.[167] The resulting expansion of the money supply supported competitive and stable markets.[176] During the mid-Ming China had gradually shifted to silver as the standard currency for large scale transactions and by the late Kangxi period, the assessment and collection of the land tax was done in silver. Landlords began only accepting rent payments in silver rather than in crops themselves, which in turn incentivized farmers to produce crops for sale in local and national markets rather than for their own personal consumption or barter.[124] Unlike the copper coins, qian or cash, used mainly for smaller transactions, silver was not reliably minted into a coin but rather was traded in units of weight: the liang or tael, which equaled roughly 1.3 ounces of silver. A third-party had to be brought in to assess the weight and purity of the silver, resulting in an extra "meltage fee" added on to the price of transaction. Furthermore, since the "meltage fee" was unregulated it was the source of corruption. The Yongzheng emperor cracked down on the corrupt "meltage fees", legalizing and regulating them so that they could be collected as a tax. From this newly increased public coffer, the Yongzheng emperor increased the salaries of the officials who collected them, further legitimising silver as the standard currency of the Qing economy.[132]
Urbanisation and the proliferation of market-towns
The second commercial revolution also had a profound effect on the dispersion of the Qing populace. Up until the late Ming there existed a stark contrast between the rural countryside and cities because extraction of surplus crops from the countryside was traditionally done by the state. However, as commercialisation expanded in the late-Ming and early-Qing, mid-sized cities began popping up to direct the flow of domestic, commercial trade. Some towns of this nature had such a large volume of trade and merchants flowing through them that they developed into full-fledged market-towns. Some of these more active market-towns even developed into small cities and became home to the new rising merchant class.[124] The proliferation of these mid-sized cities was only made possible by advancements in long-distance transportation and communication. As more and more Chinese citizens were travelling the country conducting trade they increasingly found themselves in a far-away place needing a place to stay; in response the market saw the expansion of guild halls to house these merchants.[132]
Full-fledged trade guilds emerged, which, among other things, issued regulatory codes and price schedules, and provided a place for travelling merchants to stay and conduct their business. Along with the huiguan trade guilds, guild halls dedicated to more specific professions, gongsuo, began to appear and to control commercial craft or artisanal industries such as carpentry, weaving, banking, and medicine.[132] By the nineteenth century guild halls worked to transform urban areas into cosmopolitan, multi-cultural hubs, staged theatre performances open to general public, developed real estate by pooling funds together in the style of a trust, and some even facilitated the development of social services such as maintaining streets, water supply, and sewage facilities.[124]
Trade with the West
In 1685, the Kangxi emperor legalised private maritime trade along the coast, establishing a series of customs stations in major port cities. The customs station at Guangzhou became by far the most active in foreign trade; by the late Kangxi reign, more than forty mercantile houses specialising in trade with the West had appeared. The Yongzheng emperor made a parent corporation comprising those forty individual houses in 1725 known as the Cohong system. Firmly established by 1757, the Canton Cohong was an association of thirteen business firms that had been awarded exclusive rights to conduct trade with Western merchants in Canton. Until its abolition after the Opium War in 1842, the Canton Cohong system was the only permitted avenue of Western trade into China, and thus became a booming hub of international trade.[132] By the eighteenth century, the most significant export China had was tea. British demand for tea increased exponentially up until they figured out how to grow it for themselves in the hills of northern India in the 1880s. By the end of the eighteenth century, tea exports going through the Canton Cohong system amounted to one-tenth of the revenue from taxes collected from the British and nearly the entire revenue of the British East India Company; in fact, until the early nineteenth century tea comprised ninety percent of exports leaving Canton.[132]
Revenue
The recorded revenues of the central Qing government increased little over the course of the 18th and early 19th century from 36,106,483 taels in 1725 to 43,343,978 taels in 1812 before declining to 38,600,570 taels in 1841, the land tax was the principal source of revenue for the central government with the salt, customs and poll taxes being important secondary sources.[178] Following the Opium Wars and the opening of China to foreign trade and the mid-century rebellions, two further important sources of revenue were added: the foreign maritime customs revenue and the likin revenue though only 20% of the likin revenue was actually given by the provinces to Hu Pu (board of revenue) in Beijing the rest remaining in provincial hands, the Hu Pu also managed to raise some miscellaneous taxes and increased the rate of the salt tax these measures doubled revenue by the late 19th century, this however was insufficient for the central government which was facing numerous crises and wars during the period and 9 foreign loans amounting to 40mil taels were contracted by the Qing government prior to 1890.[179]
It was estimated in the 1850s that wages around the capital of Beijing and the Yangtze delta region for a farmer was between 0.99 and 1.02 taels a month; assuming every day was worked, this would amount to roughly 12 taels a year with over 400,000,000 citizens in 1890 the level of taxation was extremely low.[180]
The Financial Reorganisation bureau of the Dynasty (established in 1909) estimated total revenue to be 292,000,000 taels. H.B. Morse estimated in the early 1900s a total of 284,150,000 taels of which 99,062,000 taels was spent by the Central government, 142,374,000 taels by the provincial governments and the remainder by the local government. In 1911 the Consultative assembly estimated total revenue to be 301,910,297 taels. Included in this figure was over 44,000,000 taels from the Likin of which only 13,000,000 was reported to Beijing.[181]
The Qing government during and following the First Sino-Japanese war increasingly took on loans to meet its expenditure requirements a total of 746,220,453 taels of which slightly over 330,000,000 taels was for Railway construction and the repayment to come from the revenues of the railways themselves thus these loans did not burden the central government finances. A relatively small sum of just over 25,500,000 taels was borrowed for industrial projects, over 5,000,000 taels for Telegraph lines with less than 1,000,000 taels for miscellaneous purposes. The remainder was primarily for the costs of the Sino-Japanese war and the indemnity in the Treaty of Shimonoseki amounting to over 382,000,000 taels.[181]
Taizu noted that these figures for formal taxation only amounted to half of the total taxation and therefore revenue of the government with these surcharges being levied at a local level by local officials who found the level of taxation far too low to support even basic governance, despite the ability to levy surcharges belonging solely to the central government.[182]
Science and technology
Chinese scholars, court academies, and local officials carried on late Ming dynasty strengths in astronomy, mathematics, and geography, as well as technologies in ceramics, metallurgy, water transport, printing. Contrary to stereotypes in some Western writing, 16th and 17th century Qing dynasty officials and literati eagerly explored the technology and science introduced by Jesuit missionaries. Manchu leaders employed Jesuits to use cannon and gunpowder to great effect in the conquest of China, and the court sponsored their research in astronomy. The aim of these efforts, however, was to reform and improve inherited science and technology, not to replace it. Scientific knowledge advanced during the Qing, but there was not a change in the way this knowledge was organised or the way scientific evidence was defined or its truth tested. Those who studied the physical universe shared their findings with each other and identified themselves as men of science, but they did not have a separate and independent professional role with its own training and advancement. They were still literati.[183]
The Opium Wars, however, demonstrated the power of steam engine and military technology that had only recently been put into practice in the West. During the Self-Strengthening Movement of the 1860s and 1870s Confucian officials in several coastal provinces established an industrial base in military technology. The introduction of railroads into China raised questions that were more political than technological. A British company built the 19 km (12 mi) Shanghai–Woosung line in 1876, obtaining the land under false pretenses, and it was soon torn up. Court officials feared local public opinion and that railways would help invaders, harm farmlands, and obstruct feng shui.[184] To keep development in Chinese hands, the Qing government borrowed 34 billion taels of silver from foreign lenders for railway construction between 1894 and 1911. As late as 1900, only 470 km (292 mi) were in operation. Finally, 8,400 km (5,200 mi) of railway was completed. The British and French after 1905 opened lines to Burma and Vietnam.[185]
Protestant missionaries by the 1830s translated and printed Western science and medical textbooks. The textbooks found homes in the rapidly enlarging network of missionary schools and universities. The textbooks opened learning open possibilities for the small number of Chinese students interested in science, and a very small number interested in technology. After 1900, Japan had a greater role in bringing modern science and technology to Chinese audiences but even then they reached chiefly the children of the rich landowning gentry.[186]
Arts and culture
Under the Qing, inherited forms of art flourished and innovations occurred at many levels and in many types. High levels of literacy, a successful publishing industry, prosperous cities, and the Confucian emphasis on cultivation all fed a lively and creative set of cultural fields.
By the end of the 19th century, national artistic and cultural worlds had begun to come to terms with the cosmopolitan culture of the West and Japan. The decision to stay within old forms or welcome Western models was now a conscious choice. Classically trained Confucian scholars such as Liang Qichao and Wang Guowei read widely and broke aesthetic and critical ground later cultivated in the New Culture Movement.
Fine arts
The Qing emperors were generally adept at poetry and often skilled in painting, and offered their patronage to Confucian culture. The Kangxi and Qianlong Emperors, for instance, embraced Chinese traditions both to control them and to proclaim their own legitimacy. The Kangxi Emperor sponsored the Peiwen Yunfu, a rhyme dictionary published in 1711, and the Kangxi Dictionary published in 1716, which remains to this day an authoritative reference. The Qianlong Emperor sponsored the largest collection of writings in Chinese history, the Complete Library of the Four Treasuries, completed in 1782. Court painters made new versions of the Song masterpiece, Zhang Zeduan's Along the River During the Qingming Festival, whose depiction of a prosperous and happy realm demonstrated the beneficence of the emperor. The emperors undertook tours of the south and commissioned monumental scrolls to depict the grandeur of the occasion.[187] Imperial patronage also encouraged the industrial production of ceramics and Chinese export porcelain. Peking glassware became popular after European glass making processes were introduced by Jesuits to Beijing.[188][189] During this period the European trend to imitate Chinese artistic traditions, known as chinoiserie also gained great popularity in Europe due to the rise in trade with China and the broader current of Orientalism.[190]
Yet the most impressive aesthetic works were done among the scholars and urban elite. Calligraphy and painting[191] remained a central interest to both court painters and scholar-officials who considered the four arts part of their cultural identity and social standing.[192] The painting of the early years of the dynasty included such painters as the orthodox Four Wangs and the individualists Bada Shanren and Shitao. Court painting of the dynasty was also greatly influenced by some Western artists.[193] The 19th century saw such innovations as the Shanghai School and the Lingnan School,[194] which used the technical skills of tradition to set the stage for modern painting.
Traditional learning and literature
Traditional learning flourished, especially among Ming loyalists such as Dai Zhen and Gu Yanwu, but scholars in the school of evidential learning made innovations in skeptical textual scholarship. Scholar-bureaucrats, including Lin Zexu and Wei Yuan, developed a school of practical statecraft which rooted bureaucratic reform and restructuring in classical philosophy.
Philosophy[195] and literature grew to new heights in the Qing period. Poetry continued as a mark of the cultivated gentleman, but women wrote in larger numbers and poets came from all walks of life. The poetry of the Qing dynasty is a lively field of research, being studied (along with the poetry of the Ming dynasty) for its association with Chinese opera, developmental trends of Classical Chinese poetry, the transition to a greater role for vernacular language, and for poetry by women. The Qing dynasty was a period of literary editing and criticism, and many of the modern popular versions of Classical Chinese poems were transmitted through Qing dynasty anthologies, such as the Complete Tang Poems and the Three Hundred Tang Poems. Although fiction did not have the prestige of poetry, novels flourished. Pu Songling brought the short story to a new level in his Strange Tales from a Chinese Studio, published in the mid-18th century, and Shen Fu demonstrated the charm of the informal memoir in Six Chapters of a Floating Life, written in the early 19th century but published only in 1877. The art of the novel reached a pinnacle in Cao Xueqin's Dream of the Red Chamber, but its combination of social commentary and psychological insight were echoed in highly skilled novels such as Wu Jingzi's The Scholars (1750) and Li Ruzhen's Flowers in the Mirror (1827).[196]
Cuisine
Cuisine aroused cultural pride. The gentleman gourmet, such as Yuan Mei, applied aesthetic standards to the art of cooking, eating, and appreciation of tea at a time when New World crops and products entered everyday life. Yuan's Suiyuan Shidan expounded culinary aesthetics and theory, along with a range of recipes. The Manchu–Han Imperial Feast originated at the court. Although this banquet was probably never common, it reflected an appreciation of Manchu culinary customs.[197]
Historiography
The Confucian concept of the dynastic cycle was used by traditional Chinese historiography to organise China's past in terms of consecutive ruling houses that arose and collapsed. The Qing dynasty was the closing chapter of the 2000-year history of Imperial China. John King Fairbank of Harvard University, a historian who is essentially credited with founding modern Chinese history in the United States, steadfastly maintained a perspective that split the history of China's past half millennium around 1842. All that fell before remained part of "traditional China", and with the Western "shock" of the First Opium War and the resulting Treaty of Nanking, "modern China" was born. The Qing dynasty was thus bifurcated in this manner. In contemporary China, there is also a similar view for such a division.[198]
The New Qing History is a revisionist historiographical school that emerged in the mid-1990s and emphasises the particular Manchu character of the dynasty. Earlier historians had emphasised a pattern of Han sinicisation of various conquerors. In the 1980s and early 1990s, American scholars began learning the Manchu language, taking advantage of archival holdings in this and other non-Chinese languages that had long been held in Taipei and Beijing but had previously attracted little scholarly attention.[199] This research concluded that the Manchu rulers 'manipulated' their subjects by fostering a sense of Manchu identity, often adopting Central Asian models of rule as much as Confucian ones.[200] The most prominent feature of the studies has been characterised by a renewed interest in the Manchus and their relationship to China and Chinese culture, as well as that of other non-Han groups ruled by Beijing.[201]
William T. Rowe of Johns Hopkins University wrote that the name "China" (中國; 中華) was generally understood to refer to the political realm of the Han Chinese during the Ming dynasty, and this understanding persisted among the Han Chinese into the early Qing dynasty, and the understanding was also shared by Aisin Gioro rulers before the Ming-Qing transition. The Qing dynasty, however, "came to refer to their more expansive empire not only as the Great Qing but also, nearly interchangeably, as China" within a few decades of this development. Instead of the earlier (Ming) idea of an ethnic Han Chinese state, this new Qing China was a "self-consciously multi-ethnic state". Han Chinese scholars had some time to adapt this, but by the 19th century, the notion of China as a multinational state with new, significantly extended borders had become the standard terminology for Han Chinese writers. Rowe noted that "these were the origins of the China we know today".[202]
See also
- Anti-Qing sentiment
- Mandarin square – costumes of Qing officials
- Foreign relations of the Qing dynasty
- Imperial Chinese harem system
- International relations (1814–1919)
- Islam during the Qing dynasty
- List of diplomatic missions of the Qing dynasty
- List of emperors of the Qing dynasty
- List of rebellions in China
- List of recipients of tribute from China
- List of Chinese monarchs
- Manchuria under Qing rule
- Military history of China before 1912
- Mongolia under Qing rule
- Qing emperors' family tree
- Qing dynasty in Inner Asia
- Qing official headwear
- The Rise and Fall of Qing Dynasty
- Royal and noble ranks of the Qing dynasty
- Taiwan under Qing rule
- Tibet under Qing rule
- Timeline of Chinese history
- Timeline of late anti-Qing rebellions
- Xinjiang under Qing rule
Notes
- ^ a b Sources consider the start year of the Qing dynasty differently, including 1644,[1][2][3][4] 1636,[5][6][7] and 1616.[8][9][10]
- ^ For other names, see Names of the Qing dynasty.
- ^ Dulimbai means 'central' or 'middle', gurun means 'nation' or 'state'
- ^ Chinese: 六部; pinyin: lìubù
- ^ 尚書; 尚书; shàngshū; Manchu: ᠠᠯᡳᡥᠠ
ᠠᠮᠪᠠᠨ, Möllendorff: aliha amban, Abkai: aliha amban - ^ 侍郎; shìláng; Manchu: ᠠᠰᡥᠠᠨ ᡳ
ᠠᠮᠪᠠᠨ, Möllendorff: ashan i amban, Abkai: ashan-i amban - ^ 內閣; 内阁; nèigé; Manchu: ᡩᠣᡵᡤᡳ
ᠶᠠᠮᡠᠨ, Möllendorff: dorgi yamun, Abkai: dorgi yamun - ^ 軍機處; 军机处; jūnjī chù; Manchu: ᠴᠣᡠ᠋ᡥᠠᡳ
ᠨᠠᠰᡥᡡᠨ ᡳ
ᠪᠠ, Möllendorff: coohai nashūn i ba, Abkai: qouhai nashvn-i ba - ^ traditional Chinese: 軍機大臣; simplified Chinese: 军机大臣; pinyin: jūnjī dàchén
- ^ Chinese: 包衣; pinyin: bāoyī; Manchu: ᠪᠣᡠ᠋ᡳ, Möllendorff: booi, Abkai: boui
References
Citations
- ^ "Ritual Music in the Court and Rulership of the Qing Dynasty (1644–1911)" (p. 136): "[1636] was the start of the Qing dynasty, although historians usually date the Qing dynasty started in 1644 when the Manchus conquered Beijing and north China."
- ^ Wasserstrom, Jeffrey N. (2022). The Oxford History of Modern China. Oxford University Press. p. ix. ISBN 978-0-19-264830-3.
- ^ Desnoyers, Charles (2017). Patterns of Modern Chinese History. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-994645-7.
- ^ Rowe (2009), p. 292.
- ^ Keliher, Macabe (2019). The Board of Rites and the Making of Qing China. University of California Press. p. ix. ISBN 978-0-520-97176-9.
- ^ Schluessel, Eric (2023). The Tarikh-i Hamidi: A Late-Qing Uyghur History. Columbia University Press. p. xv. ISBN 978-0-520-97176-9.
- ^ Elverskog, Johan (2008). Our Great Qing: The Mongols, Buddhism, and the State in Late Imperial China. University of Hawaii Press. p. 17. ISBN 978-0-8248-6381-4.
- ^ Li, Xiangmin (2024). A HISTORY OF FINE ARTS ECONOMY OF CHINA. American Academic. p. 282. ISBN 978-1-63181-470-9.
- ^ Wang, Robin (2003). Images of Women in Chinese Thought and. Hackett. p. 285. ISBN 978-0-87220-651-9.
- ^ Yang, Zhanghui (2024). Convergence of East-West Poetics. Taylor & Francis. p. 37. ISBN 978-1-04-009828-8.
- ^ Söderblom Saarela (2021).
- ^ Norman (1988), pp. 133–134.
- ^ a b c Taagepera, Rein (September 1997). "Expansion and Contraction Patterns of Large Polities: Context for Russia" (PDF). International Studies Quarterly. 41 (3): 500. doi:10.1111/0020-8833.00053. ISSN 0020-8833. JSTOR 2600793. Archived (PDF) from the original on 7 July 2020. Retrieved 24 July 2020.
- ^ Wang Jianqiang (王堅強); Chen Jiahua (陳家華); Wang Yongzhong (王永中) (2018). 歷史與時事學法指導 (in Chinese). Ningbo chubanshe. p. 8. ISBN 9787552632859.
- ^ a b Broomhall, Marshall (1907). The Chinese Empire: A General and Missionary Survey, Volumes 678–679. Morgan at Scott. pp. 2–3.
- ^ a b The Cambridge History of China: Volume 9, The Ch'ing Empire to 1800, Part 1, by Willard J. Peterson, p. 29
- ^ Rowe (2009), pp. 14–15.
- ^ Yamamuro, Shin'ichi (2006). Manchuria Under Japanese Domination. Translated by Fogel, J. A. University of Pennsylvania Press. p. 246. ISBN 978-0812239126.
- ^ Crossley (1997), pp. 212–213.
- ^ Dong, Shaoxin (2020). "The Tartars in European Missionary Writings of the Seventeenth Century". In Weststeijn, Thijs (ed.). Foreign Devils and Philosophers Cultural Encounters between the Chinese, the Dutch, and Other Europeans, 1590–1800. Leiden: Brill. pp. 82–83. ISBN 978-9004418929. Archived from the original on 8 May 2021. Retrieved 14 March 2021.
- ^ Woolley, Nathan (2016), Celestial Empire: Life in China 1644–1911, National Library of Australia, p. 107, ISBN 9780642278760
- ^ Zhao (2006), pp. 4, 7–10, 12–14 and 24 n. 4.
- ^ Bilik, Naran (2007). "Names Have Memories: History, Semantic Identity and Conflict in Mongolian and Chinese Language Use". Inner Asia. 9 (1): 34. doi:10.1163/146481707793646629.
- ^ Zhao (2006), pp. 4, 7–10, 12–14.
- ^ a b Dunnell, Ruth W.; Elliott, Mark C.; Foret, Philippe; Millward, James A. (2004). New Qing Imperial History: The Making of Inner Asian Empire at Qing Chengde. Routledge. ISBN 978-1134362226.
- ^ Ebrey (2010), p. 220.
- ^ Swope, Kenneth M. (2014). The Military Collapse of China's Ming Dynasty, 1618–44 (Illustrated ed.). Routledge. p. 16. ISBN 978-1134462094.
- ^ Mair, Victor H.; Chen, Sanping; Wood, Frances (2013). Chinese Lives: The People Who Made a Civilization (Illustrated ed.). Thames & Hudson. ISBN 978-0500771471.
- ^ a b Ebrey (2010), pp. 220–224.
- ^ Bernard Hung-Kay Luk, Amir Harrak-Contacts between cultures, Vol. 4, p. 25
- ^ Rawski (1991), p. 177.
- ^ Tumen jalafun jecen akū: Manchu studies in honour of Giovanni Stary By Giovanni Stary, Alessandra Pozzi, Juha Antero Janhunen, Michael Weiers
- ^ Li (2002), pp. 60–62.
- ^ Li (2002), p. 65.
- ^ "China". Encyclopedia Britannica. Archived from the original on 27 July 2019. Retrieved 21 July 2019.
- ^ Spence (2012), p. 32.
- ^ Di Cosmo (2007), p. 6.
- ^ Naquin & Rawski (1987), p. 141.
- ^ Di Cosmo (2007), p. 23.
- ^ Di Cosmo (2007), p. 9.
- ^ Rawski (1991), p. 175.
- ^ Di Cosmo (2007), p. 7.
- ^ Spence (1990), p. 41.
- ^ Wakeman (1985), p. 478.
- ^ Wang, Yuanchong (2018). Remaking the Chinese Empire: Manchu-Korean Relations, 1616–1911. Brighton: Cornell University Press. p. 30. ISBN 9781501730511.
- ^ a b Spence (2012), p. 38.
- ^ Wakeman (1985), pp. 646–650.
- ^ Wakeman (1985), p. 648, n. 183.
- ^ Wakeman (1985), pp. 651–680.
- ^ Faure (2007), p. 164.
- ^ Ebrey (1993), p. [page needed].
- ^ Wakeman (1977), p. 83.
- ^ This event was recorded by Italian Jesuit Martin Martinius in his account Bellum Tartaricum with original text in Latin, first published in Rome 1654. First English edition, London: John Crook, 1654.
- ^ Ho (2011), p. 135.
- ^ Ho (2011), p. 198.
- ^ Ho (2011), p. 206.
- ^ Ho (2011), p. 307.
- ^ Rowe (2009), pp. 32–33.
- ^ Kuzmin, Sergius L.; Dmitriev, Sergey (2015). "Conquest dynasties of China or foreign empires? The problem of relations between China, Yuan and Qing". International Journal of Central Asian Studies. 19: 59–92. Retrieved 14 November 2017 – via Academia.
- ^ Macabe Keliher (2019). The Board of Rites and the Making of Qing China. University of California Press. p. 3. ISBN 9780520971769.
- ^ Farquhar, David (1978). "Emperor As Bodhisattva in the Governance of the Qing Empire". Harvard Journal of Asiatic Studies. 38 (1): 5–34. doi:10.2307/2718931. JSTOR 2718931.
- ^ Kapstein, Matthew (2014). Buddhism Between Tibet and China. Wisdom. p. 185. ISBN 9780861718061.
- ^ Huiyun Feng (2020). China's Challenges and International Order Transition. University of Michigan Press. p. 151. ISBN 9780472131761.
- ^ "The Qing Dynasty and Its Central Asian Neighbors". Retrieved 17 September 2023.
- ^ Spence (2012), pp. 48–51.
- ^ Perdue (2005).
- ^ Spence (2012), pp. 62–66.
- ^ Spence (2012), pp. 97, 101.
- ^ Spence (2012), p. 72.
- ^ Hsü (1990), p. 35.
- ^ Rowe (2009), p. 68.
- ^ Hsü (1990), pp. 35–37.
- ^ Spence (2012), pp. 80–83.
- ^ Spence (2012), pp. 83, 86.
- ^ 康乾盛世"的文化專制與文字獄. china.com (in Chinese). Archived from the original on 5 January 2009. Retrieved 30 December 2008.
- ^ Schoppa, R. Keith. Revolution and its Past: Identities and Change in Modern Chinese History. Pearson Hall, 2010, pp. 42–43.
- ^ Spence (1990), pp. 112, 114, 116.
- ^ Têng & Fairbank (1954), p. 19.
- ^ Platt (2012), p. xxii.
- ^ "Taiping Rebellion". Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved 7 November 2021.
- ^ Hevia (2003).
- ^ Wright (1957), pp. 196–221.
- ^ Hsü (1990), pp. 328–330.
- ^ "California on the Amur, or the 'Zheltuga Republic' in Manchuria (1883–86)". Retrieved 9 September 2023.
- ^ Fuchs, Eckhardt (2017). A New Modern History of East Asia. V&R. p. 97. ISBN 9783737007085.
- ^ Crossley (2010), p. 117.
- ^ Reynolds (1993), pp. 35–36.
- ^ Spence (2012), pp. 223–225.
- ^ Reynolds (1993), pp. 5–11.
- ^ Hsü (1990), pp. 412–416.
- ^ Rhoads (2000), p. 121 ff.
- ^ Chien-nung Li, Jiannong Li, Ssŭ-yü Têng, "The political history of China, 1840–1928", p. 234
- ^ Billingsley (1988), pp. 56–59.
- ^ Spence (2012), p. 39.
- ^ Jackson & Hugus (1999), pp. 134–135.
- ^ Rowe (2009), pp. 211.
- ^ Zhu, Jianfei (2004). Chinese Spatial Strategies: Imperial Beijing, 1420–1911. Routledge. p. 133. ISBN 978-1-134-36620-0.
- ^ Bartlett (1991).
- ^ "The Rise of the Manchus". University of Maryland. Archived from the original on 18 December 2008. Retrieved 19 October 2008.
- ^ Chen, Albert H. Y. (2021). The Changing Legal Orders in Hong Kong and Mainland China. City University of Hong Kong Press. p. 372. ISBN 9789629374501.
- ^ Atwill, David (2021). Sources in Chinese History: Diverse Perspectives from 1644 to the Present. Taylor & Francis. p. 272. ISBN 9780429560347.
- ^ Wang Jianlang (王建朗) (2016). 两岸新编中国近代史.晚清卷 (in Chinese). Shehui kexuewen xianchubanshe. p. 530.
- ^ a b Rawski (1998), p. 179.
- ^ Rawski (1998), pp. 179–180.
- ^ Torbert (1977), p. 27.
- ^ Torbert (1977), p. 28.
- ^ Elliott 2001, p. 40.
- ^ Millward 2007, p. 95.
- ^ Davidson, James W. (1903). The Island of Formosa, Past and Present : history, people, resources, and commercial prospects : tea, camphor, sugar, gold, coal, sulphur, economical plants, and other productions. London and New York: Macmillan. OL 6931635M. pp. 247, 620.
- ^ "Treaty of Peace between China and Japan (Treaty of Shimonoseki)". Ch'ing Dynasty Treaties and Agreements Preserved by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Republic of China (Taiwan). National Palace Museum. 17 April 1895. 中國將管理下開地方之權並將該地方所有堡壘軍器工廠及一切屬公物件永遠讓於日本...台湾全岛及所有附属各岛屿...澎湖列岛 [China shall yield to Japan in perpetuity the rights to administer the following regions as well as all fortresses, munition factories, and public properties thereof ... the entire island of Taiwan and all appertaining islands ... Penghu archipelago]
- ^ Millward (2007), p. 190.
- ^ "<untitled>" (PDF). The New York Times. 19 January 1906. Archived (PDF) from the original on 26 March 2020. Retrieved 13 June 2018.
- ^ . 1906 – via Wikisource.
- ^ Rowe (2009), p. 91.
- ^ Rowe (2009), pp. 91–92.
- ^ a b Rowe (2009), p. 92.
- ^ Edmonds, Richard L. (1979). "The Willow Palisade". Annals of the Association of American Geographers. 69 (4): 599–621. doi:10.1111/j.1467-8306.1979.tb01285.x. ISSN 0004-5608. JSTOR 2563132.
- ^ Richards, John F. (2003). The Unending Frontier: An Environmental History of the Early Modern World. University of California Press. pp. 141, 144. ISBN 978-0-520-23075-0.
- ^ Lee, Robert H. G. (1970). The Manchurian frontier in Chʼing history. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press. p. 103. ISBN 978-0-674-54775-9.
- ^ "China's narrative of Han expansion". South China Morning Post. 2012. Archived from the original on 8 November 2021. Retrieved 8 November 2021.
- ^ Matsuzato, Kimitaka (2016). Russia and Its Northeast Asian Neighbors: China, Japan, and Korea, 1858–1945. Rowman & Littlefield. pp. 27–28. ISBN 978-1-4985-3705-6.
- ^ Rowe (2002), p. 485.
- ^ Naquin & Rawski (1987), p. 117.
- ^ a b c d e Rowe (2009), p. [page needed].
- ^ Rowe (2009), pp. 109–110.
- ^ Rowe (2009), pp. 112–113.
- ^ Rowe (2009), p. 111.
- ^ Rowe (2009), pp. 114–116.
- ^ Sneath (2007), p. 101.
- ^ Xu (2005), p. 335.
- ^ Rowe (2009), pp. 116–117.
- ^ a b c d e f g Porter (2016), p. [page needed].
- ^ Sneath (2007), p. 98.
- ^ Sneath (2007), pp. 105–106.
- ^ Goossaert & Palmer (2011), p. 3.
- ^ "Living in the Chinese Cosmos: Understanding Religion in Late Imperial China (1644–1911)", Religion, the State, and Imperial Legitimacy, Columbia University, archived from the original on 12 April 2021, retrieved 15 June 2021
- ^ Teiser, Stephen F. (1996). "Introduction" (PDF). In Lopez, Donald S. Jr. (ed.). The Spirits of Chinese Religion. Princeton University Press. p. 27. Archived (PDF) from the original on 24 August 2015. Retrieved 15 June 2021.
- ^ Harrison, Henrietta (2001). China. London: Arnold; New York: Oxford University Press. pp. 36–42. ISBN 0340741333..
- ^ Elliott (2001), pp. 235, 241.
- ^ Rawski (1998), pp. 231–236, 242–243.
- ^ Rawski (1998), p. 236.
- ^ Elliott (2001), pp. 237–238.
- ^ Richard J. Smith (2007). Settling the Dead: Funerals, Memorials and Beliefs Concerning the Afterlife Archived 27 September 2011 at the Wayback Machine. Living in the Chinese Cosmos: Understanding Religion in Late-Imperial China
- ^ "Living in the Chinese Cosmos: Understanding Religion in Late Imperial China (1644–1911)" (Columbia University) Institutional Religion: The Three Teachings Archived 8 May 2017 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Lagerwey (2010), pp. 6–7.
- ^ Mote, Frederick W. (1999). Imperial China, 900–1800. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press. ISBN 0674445155., pp. 958–961.
- ^ Bays (2012), pp. 21–23.
- ^ Bays (2012), pp. 25–26.
- ^ Reilly (2004), p. 43.
- ^ Reilly (2004), p. 44.
- ^ Elliott (2001), p. 241.
- ^ Daily (2013), p. 1.
- ^ Daily (2013), p. 145.
- ^ Daily (2013), pp. 188–189.
- ^ Reilly (2004), pp. 61, 64.
- ^ Reilly (2004), p. 43-50.
- ^ Reilly (2004), pp. 57, 62.
- ^ Goossaert & Palmer (2011), pp. 38–39.
- ^ Fairbank, John King (2006), China: A New History (2nd ed.), Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, pp. 221–222, ISBN 978-0674018280.
- ^ Goossaert & Palmer (2011), pp. 38–40.
- ^ Goossaert & Palmer (2011), pp. 40–41.
- ^ Mühlhahn (2019), p. 170.
- ^ Choa, Gerald H. (1990). 'Heal the Sick' was Their Motto: The Protestant Medical Missionaries in China. Chinese University Press.
- ^ Chen, Kaiyi (1996). "Missionaries and the early development of nursing in China". Nursing History Review. 4: 129–149. doi:10.1891/1062-8061.4.1.129. PMID 7581277. S2CID 34206810.
- ^ Myers & Wang (2002), pp. 564, 566.
- ^ Myers & Wang (2002), p. 564.
- ^ a b Murphey (2007), p. 151.
- ^ Myers & Wang (2002), p. 593.
- ^ Myers & Wang (2002), pp. 593, 595.
- ^ Myers & Wang (2002), p. 598.
- ^ Myers & Wang (2002), pp. 572–573, 599–600.
- ^ Myers & Wang (2002), pp. 606, 609.
- ^ Xu, Suming (2005). Tianjin Social Science 人学史观视阈下的中西大分流——对"为什么江南不是英国"之新思考 [The Great Divergence from a humanist perspective: Why was Jiangnan not England?)] (in Chinese). Vol. 6.
- ^ Li, Bo; Zheng, Yin (2001). 5000 years of Chinese history (in Chinese). Inner Mongolian People's publishing corp. ISBN 978-7-204-04420-7.
- ^ Myers & Wang (2002), p. 587.
- ^ Myers & Wang (2002), pp. 587, 590.
- ^ Haywood, John (1997). Atlas of world history. New York : Barnes & Noble Books. pp. Map 67, 71. ISBN 978-0-7607-0687-9.
- ^ Twitchett & Fairbank (1978), p. 61.
- ^ Twitchett & Fairbank (1978), pp. 61–62.
- ^ Peng, Linan (2021). "The last guardian of the throne: the regional army in the late Qing dynasty". Journal of Institutional Economics. 17 (2): 328–329. doi:10.1017/S1744137420000430. S2CID 225162563.
- ^ a b Twitchett & Fairbank (1978), pp. 63–66.
- ^ Zhang, Taizu (2023). The ideological foundations of Qing taxation:Belief systems, Politics, and institutions. Cambridge University Press. pp. 46, 69, 99. ISBN 978-1108995955.
- ^ Porter (2016), pp. 229–238.
- ^ Pong, David (1973). "Confucian patriotism and the destruction of the Woosung railway, 1877". Modern Asian Studies. 7 (3): 647–676. doi:10.1017/S0026749X00005333. JSTOR 311679. S2CID 202928323.
- ^ Harter, Jim (2005). World Railways of the Nineteenth Century. Johns Hopkins University Press. p. 223. ISBN 978-0801880896. Retrieved 10 September 2019.
- ^ Elman, Benjamin (2005). On Their Own Terms: Science in China, 1550–1900. Harvard University Press. pp. 270–331, 396. ISBN 978-0674016859.
- ^ "Recording the Grandeur of the Qing". The Metropolitan Museum of Art, Columbia University. Archived from the original on 20 December 2012. Retrieved 17 May 2020. Chinese painting
- ^ Boda, Yang. Study of glass wares from the Qing Dynasty (1644–1911). 1983.
- ^ Nilsson, Jan-Erik. "Chinese Porcelain Glossary: Glass, Chinese (Peking Glass)". gotheborg.com. Archived from the original on 14 February 2022. Retrieved 7 June 2017.
- ^ Beevers, David (2009). Chinese Whispers: Chinoiserie in Britain, 1650–1930. Brighton: Royal Pavilion & Museums. p. 19. ISBN 978-0-948723-71-1.
- ^ "Ch'ing Dynasty – The Art of Asia – Chinese Dynasty Guide". www.artsmia.org. Archived from the original on 27 September 2012. Retrieved 13 September 2012.
- ^ "Qing Dynasty, Painting". The Met. Metropolitan Museum of Art. Archived from the original on 20 September 2012. Retrieved 13 September 2012.
- ^ "Transcultural Dialogues: The Journey of East Asian Art to The West". Fu Qiumeng. Retrieved 25 November 2024.
- ^ "Home". The Lingnan School of Painting. Archived from the original on 8 July 2012.
- ^ Ng, On-cho (2019). "Qing Philosophy". In Zalta, Edward N. (ed.). The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (Summer 2019 ed.). Metaphysics Research Lab, Stanford University. Archived from the original on 16 June 2020. Retrieved 18 January 2020.
- ^ "Ming and Qing Novels" (PDF). Berkshire Encyclopedia. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 June 2013. Retrieved 13 September 2012.
- ^ Spence, Jonathan (1977). ""Ch'ing"". In Kwang-chih Chang (ed.). Food in Chinese Culture: Anthropological and Historical Perspectives. New Haven, CT: Yale University Press. pp. 260–294.
Reprinted in Spence, Jonathan (1992). Chinese Roundabout: Essays in History and Culture. New York: W. W. Norton. - ^ Rowe (2009), pp. 2–3.
- ^ Waley-Cohen (2004), pp. 194–197.
- ^ Rawski, Evelyn (1996). "Reenvisioning the Qing: The Significance of the Qing Period in Chinese History". Journal of Asian Studies. 55 (4): 829–850. doi:10.2307/2646525. JSTOR 2646525. S2CID 162388379.
- ^ Dunnell, Ruth (2004). New Qing Imperial History: The Making of Inner Asian Empire at Qing Chengde. Taylor & Francis. p. 3. ISBN 9781134362226.
- ^ Rowe (2009), pp. 210–211.
Sources
- Bartlett, Beatrice S. (1991). Monarchs and Ministers: The Grand Council in Mid-Ch'ing China, 1723–1820. University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-06591-8.
- Bays, Daniel H. (2012). A New History of Christianity in China. Chichester: Wiley-Blackwell. ISBN 978-1405159548.
- Billingsley, Phil (1988). Bandits in Republican China. Stanford University Press. ISBN 978-0-804-71406-8.
- Crossley, Pamela Kyle (1997). The Manchus. Wiley. ISBN 978-1-55786-560-1.
- ——— (2010). The Wobbling Pivot: China since 1800. Malden, MA: Wiley-Blackwell. ISBN 978-1-4051-6079-7.
- Daily, Christopher A. (2013). Robert Morrison and the Protestant Plan for China. Hong Kong University Press. ISBN 978-9888208036.
- Deng, Kent (2015). China's Population Expansion and Its Causes during the Qing Period, 1644–1911 (PDF).
- Di Cosmo, Nicola, ed. (2007). The Diary of a Manchu Soldier in Seventeenth Century China: "My Service in the Army," by Dzengseo. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-135-78955-8.
- Ebrey, Patricia (1993). Chinese Civilization: A Sourcebook (2nd ed.). New York: Simon and Schuster. ISBN 978-0-02-908752-7.
- ——— (2010). The Cambridge Illustrated History of China. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-12433-1.
- ——; Walthall, Anne (2013). East Asia: A Cultural, Social, and Political History (3rd ed.). Cengage. ISBN 978-1-285-52867-0. Retrieved 1 September 2015.
- Elliott, Mark C. (2001). The Manchu Way: The Eight Banners and Ethnic Identity in Late Imperial China. Stanford University Press. ISBN 978-0-8047-4684-7.
- Faure, David (2007). Emperor and Ancestor: State and Lineage in South China. Stanford University Press. ISBN 978-0-8047-5318-0.
- Goossaert, Vincent; Palmer, David A. (2011). The Religious Question in Modern China. Chicago: Chicago University Press. ISBN 978-0226304168.
- Hevia, James L. (2003). English Lessons: The Pedagogy of Imperialism in Nineteenth-Century China. Duke University Press. ISBN 978-0822331889.
- Ho, David Dahpon (2011). Sealords Live in Vain: Fujian and the Making of a Maritime Frontier in Seventeenth-Century China (Thesis). San Diego: University of California. Archived from the original on 29 June 2016. Retrieved 17 June 2016.
- Hsü, Immanuel C. Y. (1990). The rise of modern China (4th ed.). New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-505867-3.
- Jackson, Beverly; Hugus, David (1999). Ladder to the Clouds: Intrigue and Tradition in Chinese Rank. Ten Speed Press. ISBN 978-1-580-08020-0.
- Lagerwey, John (2010). China: A Religious State. Hong Kong University Press. ISBN 978-9888028047.
- Li, Gertraude Roth (2002). "State building before 1644". In Peterson, Willard J. (ed.). The Cambridge History of China, Volume 9: The Ch'ing Empire to 1800, Part One. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 9–72. ISBN 978-0-521-24334-6.
- Millward, James A. (2007). Eurasian crossroads: a history of Xinjiang. Columbia University Press. ISBN 978-0-231-13924-3. Retrieved 18 May 2020.
- Mühlhahn, Klaus (2019). Making China Modern: From the Great Qing to Xi Jinping. Harvard University Press. pp. 21–227. ISBN 978-0-674-73735-8.
- Murphey, Rhoads (2007). East Asia: A New History (4th ed.). Pearson Longman. ISBN 978-0-321-42141-8.
- Myers, H. Ramon; Wang, Yeh-Chien (2002). "Economic developments, 1644–1800". In Peterson, Willard J. (ed.). The Cambridge History of China, Volume 9: The Ch'ing Empire to 1800, Part One. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 563–647. ISBN 978-0-521-24334-6.
- Naquin, Susan; Rawski, Evelyn Sakakida (1987). Chinese Society in the Eighteenth Century. Yale University Press. ISBN 978-0-300-04602-1.
- Norman, Jerry (1988). Chinese. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0521228093.
- Perdue, Peter C. (2005). China Marches West: The Qing Conquest of Central Eurasia. Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-674-01684-2.
- Platt, Stephen R. (2012). Autumn in the Heavenly Kingdom: China, the West, and the Epic Story of the Taiping Civil War. Alfred A. Knopf. ISBN 978-0-307-27173-0.
- Porter, Jonathan (2016). Imperial China, 1350–1900. Lanham: Rowman & Littlefield. ISBN 978-1-442-22293-9.
- Rawski, Evelyn S. (1991). "Ch'ing Imperial Marriage and Problems of Rulership". In Rubie Sharon Watson; Patricia Buckley Ebrey (eds.). Marriage and Inequality in Chinese Society. University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-06930-5.
- —— (1998). The Last Emperors: A Social History of Qing Imperial Institutions. University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-21289-3.
- Reilly, Thomas H. (2004). The Taiping Heavenly Kingdom: Rebellion and the Blasphemy of Empire. Seattle: University of Washington Press. ISBN 978-0295801926.
- Rhoads, Edward J. M. (2000). Manchus & Han: Ethnic Relations and Political Power in Late Qing and Early Republican China, 1861–1928. Seattle: University of Washington Press. ISBN 0295979380. Retrieved 2 October 2021.
- Reynolds, Douglas Robertson (1993). China, 1898–1912: The Xinzheng Revolution and Japan. Cambridge, MA: Council on East Asian Studies, Harvard University. ISBN 978-0-674-11660-3.
- Rowe, William T. (2002). "Social stability and social change". In Peterson, Willard J. (ed.). The Cambridge History of China, Volume 9: The Ch'ing Empire to 1800, Part One. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 473–562. ISBN 978-0-521-24334-6.
- —— (2009). China's Last Empire: The Great Qing. History of Imperial China. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-674-03612-3.
- Sneath, David (2007). The Headless State: Aristocratic Orders, Kinship Society, and Misrepresentations of Nomadic Inner Asia (illustrated ed.). Columbia University Press. ISBN 978-0-231-51167-4.
- Söderblom Saarela, Mårten (2021). "Manchu Language". Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Asian History. Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/acrefore/9780190277727.013.447. ISBN 978-0-19-027772-7.
- Spence, Jonathan D. (1990). The Search for Modern China (1st ed.). New York: Norton. ISBN 978-0-393-30780-1. Online at Internet Archive
- ——— (2012). The Search for Modern China (3rd ed.). New York: Norton. ISBN 978-0-393-93451-9.
- Têng, Ssu-yü; Fairbank, John King, eds. (1954) [reprint 1979]. China's Response to the West: A Documentary Survey, 1839–1923. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-674-12025-9.
- Torbert, Preston M. (1977). The Ch'ing Imperial Household Department: A Study of Its Organization and Principal Functions, 1662–1796. Harvard University Asia Center. ISBN 978-0-674-12761-6.
- Twitchett, Denis Crispin; Fairbank, John King (1978). The Cambridge history of China. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-24327-8.
- Wakeman, Frederic Jr. (1977). The Fall of Imperial China. Transformation of modern China series. New York: Free Press. ISBN 978-0-02-933680-9.
- ——— (1985). The Great Enterprise: The Manchu Reconstruction of Imperial Order in Seventeenth-century China. Vol. I. University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-04804-1.
- Waley-Cohen, Joanna (2004). "The New Qing History". Radical History Review. 88 (1): 193–206. doi:10.1215/01636545-2004-88-193. S2CID 144544216.
- Wright, Mary Clabaugh (1957). The Last Stand of Chinese Conservatism: The T'ung-Chih Restoration, 1862–1874. Stanford University Press. ISBN 978-0-804-70475-5.
- Xu, Xiaoman (2005). ""Preserving the Bonds of Kin": Genealogy Masters and Genealogy Production in the Jiangsu-Zhejiang Area in the Qing and Republican Periods". In Brokaw, Cynthia J.; Chow, Kai-wing (eds.). Printing and Book Culture in Late Imperial China. Translated by Huang, Yuanmei. Berkeley: University of California. ISBN 978-0520231269.
- Zhao, Gang (2006). "Reinventing China Imperial Qing Ideology and the Rise of Modern Chinese National Identity in the Early Twentieth Century" (PDF). Modern China. 32 (1): 3–30. doi:10.1177/0097700405282349. JSTOR 20062627. S2CID 144587815. Archived from the original (PDF) on 25 March 2014.
External links
- Section on the Ming and Qing dynasties of "China's Population: Readings and Maps."
- Collection: "Manchu, Qing Dynasty"[permanent dead link] from the University of Michigan Museum of Art
- Qing Dynasty resource Archived 24 November 2020 at the Wayback Machine at the Virginia Museum of Fine Arts

