အနောက်ရှားနယ်
| Western Xia | |
|---|---|
 | |
 | |
| မြို့တော် | Xingqing (modern Yinchuan) |
| ကိုးကွယ်မှု | Primary: Buddhism Secondary: Taoism Confucianism Chinese folk religion |
| အစိုးရ | Monarchy |
| ငွေကြေး | Barter with some copper coins in the cities (see: Western Xia coinage)[၁] |
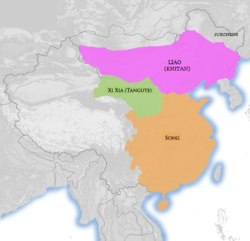
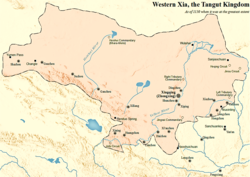
အနောက်ရှားနယ် (သို) ရှီရှားနယ် ( တရုတ်: 西夏 )ကို တန်ဂုအင်ပါယာအဖြစ် မွန်ဂိုများနှင့် တန်ဂုလူမျိုး တို့ကမှတ်ယူကြသည်။ တိဘတ်တို့က တန်ဂုတို့ကို မိညာဂ်ဟုခေါ်ကြသည်။ [၂] တရုတ်ပြည် အနောက်မြောက်ပိုင်းတွင် တန်ဂုအင်ပါယာအဖြစ်တည်ရှိခဲ့ပြီးထိုအင်ပါယာတွင် ၁၀၃၈ခုနှစ်မှ ၁၂၂၇ခုနှစ်အထိပါဝင်သည့်နယ်မြေများမှာ ယနေ့ခေတ် တရုတ်ပြည်ရှိ နယ်မြေများတွင် Ningxia, Gansu ကွင်ဟိုင်း အရှေ့ပိုင်း၊ ရှန်စီ မြောက်ပိုင်း၊ ရှင်ဂျန် အရှေ့မြောက်ပိုင်း၊ အတွင်းပိုင်းမွန်ဂိုလီးယား အနောက်တောင်ဘက်နှင့် မွန်ဂိုလီးယား တောင်ဘက်စွန်ထိစုစုပေါင်းတိုင်းတာလျှင် အကျယ်မှာ ၈၀၀,၀၀၀ စတုရန်း ကီလိုမီတာ (၃၁၀,၀၀၀ စတုရန်းမိုင်) ရှိသည်။ [၃] [၄] [၅] ထိုဒေသ၏ မြို့တော်မှာ ရှီချင် (ခေတ်သစ် Yinchuan ) ထိုဒေသကို မွန်ဂို မကျူးကျော်ခင် ၁၂၂၇ ခုနှစ်အထိ မပျက်မစီးတည်ရှိခဲ့သည်။ မကျူးကျော်ခင်အထိ ထိုသူတို့ ရေးသားချက်များနှင့်ဗိသု တည်ရှိခဲ့ပါပြီး အများစုမှာ ဖျက်ဆီးခြင်းခံခဲ့ရပြီး ၂၀ရာစု တရုတ်ပြည်တည်ထောင်ပြီးကာစကာလရောက်ရှိလာချိန်တွင် တရုတ်ပြည်အနောက်ပိုင်းတွင် ထိုအင်ပါယာကိုတည်ထောင်ခဲ့သူများနှင့်သမိုင်းမှတ်တမ်းများကို မရှာဖွေနိုင်ကြတော့ပေ။
၁၂၂၆ ခုနှစ်ဩဂုတ်လတွင်မွန်ဂိုတပ်များသည်အနောက်မြောက် Xia အင်ပါယာ၏ဒုတိယအကြီးဆုံးမြို့ဖြစ်သော ၀ ီဝေ သို့ချဉ်းကပ်ကာဖျက်ဆီးခြင်းမှလွတ်မြောက်ရန်ခုခံခြင်းမရှိဘဲလက်နက်ချခဲ့သည်။ [၆] ဤအချိန်တွင် ianကရာဇ် Xianzong ကွယ်လွန်သွားပြီးနောက်သူ၏ဆွေမျိုး Westernကရာဇ်အနောက်ရှိ Xia မှ မိုဇူ သည်မွန်ဂိုတို့၏ကျူးကျော်မှုကိုကိုင်တွယ်ဖြေရှင်းခဲ့သည်။ ၁၂၂၆ ဆောင်း ဦး ရာသီတွင် Genghis Liang စီရင်စု ကိုယူပြီး Helan တောင်တန်းများ ကိုဖြတ်ကျော်ခဲ့သည်။ နိုဝင်ဘာလတွင် Yinchuan မှကီလိုမီတာ ၃၀ သာဝေးသော Lingwu သို့ဝိုင်းရံခဲ့သည်။ [၇] [၈] ဒီနေရာမှာ မြစ်ဝါတိုက်ပွဲမှာ မွန်ဂိုတွေဟာအနောက် Xia စစ်သား ၃၀၀၀၀၀ ကိုဖျက်ဆီးခဲ့ပြီးသူတို့ကိုဆန့်ကျင်တိုက်ခိုက်ခဲ့တယ်။ [၉]
Genghis, 1227 ခုနှစ်တွင်မြို့ကိုဝိုင်းထား Yinchuan ရောက်ရှိနေပြီနှင့်တဦးတည်းအင်အားစုအဖြစ်ဝေးသောအဖြစ်ရောက်ရှိအတူအနောက်တိုင်း Xia မှစစ်ကူပို့ခြင်းမှသူတို့ကိုကာကွယ်တားဆီးဖို့ Jin ကသို့အကြိမ်ကြိမ်ထိုးစစ်များစတင် Kaifeng, အ Jin ကမြို့တော်။ [၁၀] Yinchuan သည်ခြောက်လခန့်ဝိုင်းရံပိတ်ဆို့ခံရပြီးနောက် Genghis သည်negotiationsကရာဇ်မင်းအားလျှို့ဝှက်စွာသတ်ဖြတ်ရန်ရည်ရွယ်ချက်ဖြင့်ငြိမ်းချမ်းရေးဆွေးနွေးပွဲများစတင်ခဲ့သည်။ [၁၁] ငြိမ်းချမ်းရေးစေ့စပ်ညှိနှိုင်းမှုကာလအတွင်းဂင်းသည် Guyuan အနီးရှိ Liupan တောင်တန်းများတ လျှောက်စစ်ဆင်ရေးများကိုဆက်လက်ပြုလုပ်ခဲ့ပြီး Jin ထံမှငြိမ်းချမ်းရေးကမ်းလှမ်းချက်ကိုငြင်းပယ်ခဲ့ပြီး Song နှင့်နယ်စပ်အနီးတွင်ကျူးကျော်ရန်ပြင်ဆင်ခဲ့သည်။ [၁၂] [၁၃] သို့သော်ဩဂုတ်လ ၁၂၂၇ တွင်ဂင်ဟစ်သည်သမိုင်းကြောင်းအရမသေချာမရေရာသောအကြောင်းကြောင့်သေဆုံးခဲ့ပြီးဆက်လက်ဖြစ်ပွားနေသောမဲဆွယ်စည်းရုံးရေးကိုမထိခိုက်စေရန်သူ၏သေဆုံးမှုကိုလျှို့ဝှက်ထားခဲ့သည်။ [၁၄] [၁၅] စက်တင်ဘာ ၁၂၂၇ တွင်Mozကရာဇ်မိုဂျူးသည်မွန်ဂိုတို့လက်သို့လက်နက်ချခဲ့ပြီးချက်ချင်းကွပ်မျက်ခဲ့သည်။ [၁၆] ထို့နောက်မွန်ဂိုတို့သည် Yinchuan ကိုလုယူခဲ့သည်၊ လူ ဦး ရေကိုသတ်ဖြတ်သည်၊ အနောက်ဘက်ရှိtombကရာဇ်သင်္ချိုင်းများကိုလုယူပြီးအနောက် Xia ပြည်နယ်အားထိရောက်စွာဖျက်ဆီးပစ်ခဲ့သည်။ [၁၇] [၁၈] [၁၉]
ဒုတိယမဲဆွယ်စည်းရုံးရေးကာလအတွင်းအနောက် Xia ကိုဖျက်ဆီးခြင်းသည်လုံးဝနီးပါးဖြစ်ခဲ့သည်။ John Man ၏အဆိုအရအနောက် Xia သည် Genghis Khan ၏မူဝါဒအပြည့်အစုံကြောင့်ထိုနယ်ပယ်မှကျွမ်းကျင်သူများ မှလွဲ၍ မည်သူတစ် ဦး တစ်ယောက်မျှမသိရှိပါ။ သူက "ဒါဟာ လူမျိုးတုံးသတ်ဖြတ်မှုကို ပထမဆုံးအကြိမ်မှတ်တမ်းတင်ခဲ့တဲ့ဥပမာဖြစ်တယ်လို့ပြောနိုင်တယ်။ ဒါဟာဆက်ဆက်အလွန်အောင်မြင်သောခဲ့ မည်ဆိုလျှင် ။ " [၂၀] သို့သော်အနောက်တိုင်း Xia တော်ဝင်မျိုးနွယ်စုအချို့အဖွဲ့ဝင်များသည်အနောက်တိုင်းမှပြောင်းရွှေ့အခြေချ စီချွမ် မြောက်ပိုင်း တိဘက် ပင်ဖြစ်နိုင်သည် အရှေ့မြောက်အိန္ဒိယ ဒေသခံအစိုးရသောမင်းတို့ဖြစ်လာတချို့ဖြစ်ရပ်အတွက်။ [၂၁] Yalong မြစ် ၏အထက်ပိုင်းတစ်လျှောက်တွင်တိဘက်၌ Western Xia ပြည်နယ်ငယ်လေးကိုတည်ထောင်ခဲ့ပြီးအခြားအနောက်နိုင်ငံများသည်ယခုခေတ် Henan နှင့် Hebei ပြည်နယ်များကိုအခြေချနေထိုင်ခဲ့ကြသည်။ [၂၂] တရုတ်ပြည်တွင်အနောက် Xia မှအကြွင်းအကျန်များသည် မင်းဆက် အလယ်၌ဆက်ရှိနေသည်။ [၂၃] [၂၄]
ယဉ်ကျေးမှု
[ပြင်ဆင်ရန်]တိုင်းပြည်သည်ဖွံဖြိုးလာသည့်အခါ၌ ယခုအခါမျိုးသုဉ်းပျောက်ကွယ်နေသော တိဘက် - ဗမာဘာသာစကား ဖြစ်သည့် ၎င်းတို့၏ တန်ဂုဘာသာစကားကို ရေးသားရန် ကိုယ်ပိုင် တန်ဂုအက္ခရာ ကိုတီထွင်ခဲ့ကြသည်။ [၂] [၂၅]
နိုင်ငံတော်၏စီးပွားရေးသည်အဓိကအားဖြင့်လယ်ယာစိုက်ပျိုးရေး၊ သင်းအုပ်ဆရာနှင့်ကုန်သွယ်ရေး (အထူးသဖြင့်အာရှအလယ်ပိုင်းနှင့်) ဖြစ်သည်။ [၂၆] [၂၇]
အနောက်ရှားနယ် ရှိ တန္တရစ်ဗုဒ္ဓဘာသာ ထုံးတမ်းစဉ်လာများသည်လိင်မှုဆိုင်ရာထုံးတမ်းဓလေ့များပျံ့နှံ့စေခဲ့သည်။ သူတို့သည်အသက် ၃၀ အရွယ်သို့ရောက်ရှိသောအမျိုးသားများနှင့်လက်ထပ်ခြင်းမပြုမီ ၁၂ ရာစုရှိ ရှန်ရှီ အွီဂါးရ်အမျိုးသမီးများသည်ဟန်တရုတ်အမျိုးသားများနှင့် လက်ထပ်ပြီးနောက်ကလေးများစွာ ရရှိခဲ့ကြသည်။ သူမသည် တရုတ်လင်ယောက်ျားများ၏ ဇနီးအဖြစ်ခံယူကြပြီး နောက်၌ တရားဝင်ဇနီးဖြစ်လာကြသည်။ [၂၈] [၂၉] [၃၀]
-
၁၂ရာစု၊ အနောက်ရှားမင်းဆက်လက်ထက်၊ ရွှံ့စေးဖြင့်ပြုလုပ်ထားသည် ဗုဒ္ဓ ဦးခေါင်းတော်
-
အနောက် Xia မင်းဆက်၏မီးခိုးရောင်အိုးဖြင့်ပြုလုပ်ထားသောတောင်ပံ kalavinka
-
Tangut ဦး ဆောင်သောအနောက် Xia မင်းဆက်မှတရုတ်လူမျိုး Gansu ၏ Yulin Caves မှဗုဒ္ဓဘာသာ manjusri ၏ပန်းချီကားတစ်ချပ်
-
Ningxia ရှိ Western Xia imperကရာဇ်သင်္ချိုင်းဂူအမှတ် ၃
-
တန်ဂွတ်အရာရှိများ
-
တန်ဂွတ် ပုံနှိပ်တိုက်
-
တန်ဂို ရွှေ့နိုင်သောအမျိုးအစားပုံနှိပ်
ကြည့်ရှုပါ
[ပြင်ဆင်ရန်]- တန်ဂုလူမျိုး
- နာမ်ဗေဒ
- တန်ဂုစာအုပ်များ
- အရှေ့ပိုင်းရှားနယ်
- တရုတ်သမိုင်း
- တရုတ်သမိုင်းကြောင်းရှိတိုင်းရင်းသားအုပ်စုများ
- Khara-Khoto
- ရုပ်ပွားတော်တစ်ရာ့ရှစ်ဆူ
- ဟောင်ဖိုဘုရား
ကိုးကား
[ပြင်ဆင်ရန်]- ↑ Chinaknowledge.de Chinese History - Western Xia Empire Economy. 2000 ff. © Ulrich Theobald. Retrieved: 13 July 2017.
- ↑ ၂.၀ ၂.၁ Stein (1972), pp. 70–71.
- ↑ Wang, Tianshun [王天顺] (1993). Xixia zhan shi [The Battle History of Western Xia] 西夏战史. Yinchuan [银川], Ningxia ren min chu ban she [Ningxia People's Press] 宁夏人民出版社.
- ↑ Bian, Ren [边人] (2005). Xixia: xiao shi zai li shi ji yi zhong de guo du [Western Xia: the kingdom lost in historical memories] 西夏: 消逝在历史记忆中的国度. Beijing [北京], Wai wen chu ban she [Foreign Language Press] 外文出版社.
- ↑ Li, Fanwen [李范文] (2005). Xixia tong shi [Comprehensive History of Western Xia] 西夏通史. Beijing [北京] and Yinchuan [银川], Ren min chu ban she [People's Press] 人民出版社; Ningxia ren min chu ban she [Ningxia People's Press] 宁夏人民出版社.
- ↑ Man၊ John (2004)။ Genghis Khan: Life, Death, and Resurrection။ New York City: St. Martin's Press။ p. 213။ ISBN 9780312366247။
- ↑ Man၊ John (2004)။ Genghis Khan: Life, Death, and Resurrection။ New York City: St. Martin's Press။ p. 214။ ISBN 9780312366247။
- ↑ Hartog 2004, pg. 134
- ↑ A Global Chronology of Conflict: From the Ancient World to the Modern Middle East: From the Ancient World to the Modern Middle East။ Santa Barbara, California: ABC-CLIO။ 2010။ p. 276။ ISBN 978-1851096725။
- ↑ de Hartog၊ Leo (2004)။ Genghis Khan: Conqueror of the World။ New York City: I.B. Tauris။ p. 135။ ISBN 1860649726။
- ↑ Man၊ John (2004)။ Genghis Khan: Life, Death, and Resurrection။ New York City: St. Martin's Press။ p. 219။ ISBN 9780312366247။
- ↑ Man၊ John (2004)။ Genghis Khan: Life, Death, and Resurrection။ New York City: St. Martin's Press။ ISBN 9780312366247။
- ↑ de Hartog၊ Leo (2004)။ Genghis Khan: Conqueror of the World။ New York City: I.B. Tauris။ p. 137။ ISBN 1860649726။
- ↑ Lange၊ Brenda (2003)။ Genghis Khan။ New York City: Infobase Publishing။ p. 71။ ISBN 9780791072226။
- ↑ Man၊ John (2004)။ Genghis Khan: Life, Death, and Resurrection။ New York City: St. Martin's Press။ p. 238။ ISBN 9780312366247။
- ↑ Sinor၊ D. (1998)။ The Uighurs, the Kyrgyz and the Tangut (Eighth to the Thirteenth Century)။ Paris: UNESCO။ p. 214။ ISBN 9231034677။
- ↑ Ebrey၊ Patricia Buckley (2012)။ East Asia: A Cultural, Social, and Political History။ Stamford, Connecticut: Cengage Learning။ p. 199။ ISBN 9781133606475။
- ↑ Mote၊ Frederick W. (1999)။ Imperial China: 900-1800။ Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press။ p. 256။ ISBN 0674012127။
- ↑ The Territories of the People's Republic of China။ London: Europa Publications။ 2002။ p. 215။ ISBN 9780203403112။
- ↑ Man၊ John (2004)။ Genghis Khan: Life, Death, and Resurrection။ New York City: St. Martin's Press။ pp. 116–117။ ISBN 9780312366247။
- ↑ Franke, Herbert and Twitchett, Denis, ed. (1995). The Cambridge History of China: Vol. VI: Alien Regimes & Border States, 907–1368. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pg. 214.
- ↑ Mote 1999, pg. 256
- ↑ Mote၊ Frederick W. (1999)။ Imperial China: 900-1800။ Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press။ pp. 256–257။ ISBN 0674012127။
- ↑ Frederick W. Mote (2003)။ Imperial China 900-1800။ Harvard University Press။ pp. 256–7။ ISBN 978-0-674-01212-7။
- ↑ Leffman, et al. (2005), p. 988.
- ↑ China: A Cultural and Historical Dictionary။ London: Curzon Press။ 1998။ p. 351။ ISBN 0-7007-0439-6။
- ↑ Rossabi၊ Morris (2014)။ A History of China။ Wiley-Blackwell။ p. 195။ ISBN 978-1-57718-113-2။
- ↑ Michal Biran။ The Empire of the Qara Khitai in Eurasian History: Between China and the Islamic World။ Cambridge University Press။ pp. 164–။ ISBN 978-0-521-84226-6။
- ↑ Dunnell၊ Ruth W. (1983)။ Tanguts and the Tangut State of Ta Hsia။ Princeton University။, page 228
- ↑ 洪၊ 皓။ 松漠紀聞။






