Quasi-star
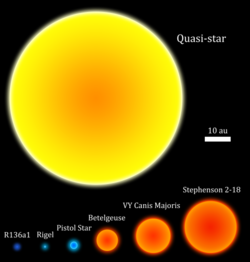
A quasi-star, also known as black hole star, is a hypothetical type of star believed to have existed in the beginning of the universe when most of the existing material was hydrogen and helium. Instead of a normal nuclear fusion core, the core of a quasi-star would be a black hole.
Formation and properties
[change | change source]Quasi-stars are stars that were so massive that while they were still alive, their cores became a black hole. But, the quasi-star didn't go supernova like in normal stars today. The star was so big that the supernova happening inside the star didn't destroy it.
These quasi-stars might have been made in dark matter halos. The gravity of these dark matter halos brought in a lot of gas, which created very big stars.
Normally in stars today, nuclear fusion stops the star's gravity from crushing it. But in quasi-stars, the black hole inside causes matter from the star to move around it. This releases a lot of energy and stops the star's gravity from crushing the star.
Quasi-stars lived for about 7 million years. The black hole at the center of the star could grow up to 1,000 to 10,000 solar masses. If quasi-stars existed the black holes they created could have become the supermassive black holes we see at the center of most galaxies, including our own Milky Way.[1] Quasi-stars were very very very big, as big as our solar system. They were also as bright and heavy as a small galaxy.[2]
Related pages
[change | change source]References
[change | change source]- ↑ Schleicher, Dominik R. G.; Palla, Francesco; Ferrara, Andrea; Galli, Daniele; Latif, Muhammad (2013-10-01). "Massive black hole factories: Supermassive and quasi-star formation in primordial halos". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 558: A59. arXiv:1305.5923. Bibcode:2013A&A...558A..59S. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201321949. ISSN 0004-6361. S2CID 119197147.
- ↑ Abramowicz, Marek (August 1982). "Twinkle, twinkle quasi star…". Nature. 298 (5877): 789–790. Bibcode:1982Natur.298..789A. doi:10.1038/298789a0. ISSN 0028-0836. S2CID 45589556.